|
The Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 19 by Larry P. Taylor, Ph. D.
Feedback appreciated; please send comments to: Email: lpt Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute The University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI |
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences FGFR Sequences
The Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 19
The most studied FGF species, FGF 1 and FGF 2, bind to all of the known FGF receptors. FGF 19, in sharp contrast, binds only to FGF 4.
The unit cell for FGF 19 is
shown in Kinemage 1. Kinemage 2 adds
ribbon rendering and Kinemage 3 shows the secondary
structure cartoon for the unit cell. The characteristics of the unit cell for
this structure are summarized at pdbsum.
FGF 19 has 2 disulphide bonds. This is unique among previously crystallized (FGF 1, 2, 4, 7, 9, & 10)
FGF molecules. Since it has the lowest sequence identity among the 23 known FGF proteins, it is considered the most divergent FGF protein. It also shows an extended C-terminal end and a flexible (13 residues which are not resolved in the X-ray experiment) portion corresponding to beta strand 11 in FGF 1 and 2. The disulphide links stabilize the loop regions that are different in FGF 19.
Cys-120 (involved in a disulphide link to Cys-102) is the only amino acid absolutely conserved across all known FGF sequences. The significance of this conservation is unknown,
FGF-19 shows an extended loop in the region corresponding to the FGF 2 turn between beta sheets 1 and 2. The disulphide bridge connecting Cys-58 to Cys-70 would stabilize this loop. In addition, the captured sulfate ion
(Kinemage 4 ) forms hydrogen bonds with the amide backbone of residues His-53, Leu-35, and Ser-56. Since this is in the region where the FGF ligand interacts with heparin and Domain 3 of the FGF receptors, this extended loop undoubtedly is a contributor to differences in physiological response of FGF 19 compared to FGF 1 and 2.
.
The most striking feature of the FGF crystal structure is the inability to resolve the loop corresponding to beta sheet 11 in other FGF molecules. This suggests a conformational mobility in this region of the molecule not seen in other FGF species. This altered loop region may explain the observed decrease (compared to FGF 1 and 2) in FGF 19 binding to heparin
This difference (comparison to FGF 2) is highlighted in Kinemage
5
In summary, the divergence in biological activity of FGF 19 can be explained by a structure that has significant structural differences compared to other FGF species.
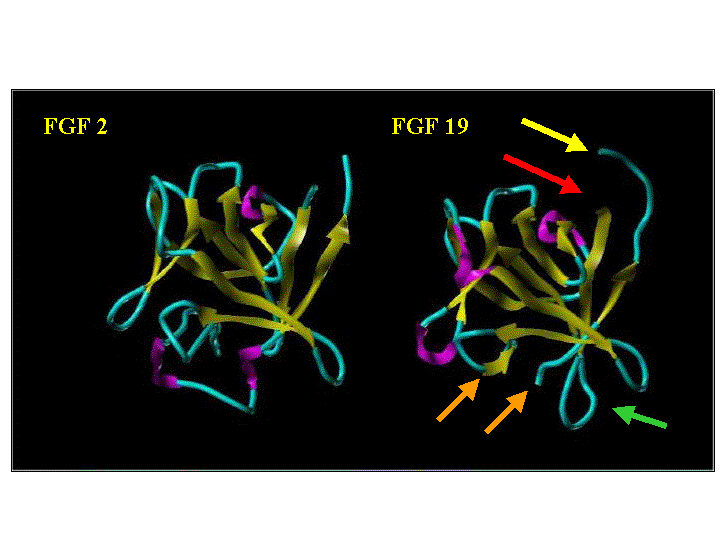
Ribbon Cartoon of FGF 2 and FGF 19

|
Arrow Color |
Description | Ribbon Color | Description | |
| Red | N-terminal End | Magenta | alpha | |
| Yellow | C-terminal End | Yellow | beta | |
| Green | Extended Loop | Cyan | coil | |
| Orange | Unresolved Loop |
The Kinemages
The real-time visualization using KiNG of the structures on this site requires a java-enabled (JRE from Java) browser.
Possible Icons to the left of molecular model image on the download page
| Java Not Activated | Java Not Activated | Java Functional |
 |
Blank Area
or message: Image requires a Java enabled browser
|
 |
| KiNG Inactive | KiNG Inactive | KiNG Full Functional |
A single click on the KiNG logo will launch the appropriate kinemage.
Kinemage 1: Calpha Backbone Trace of FGF 19
|
24 K |
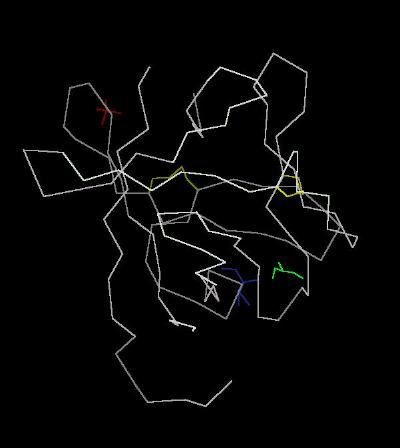 |
| Click on KiNG to see | Calpha Trace of FGF 19 |
Kinemage 2: Ribbon View of FGF 19
|
215 K |
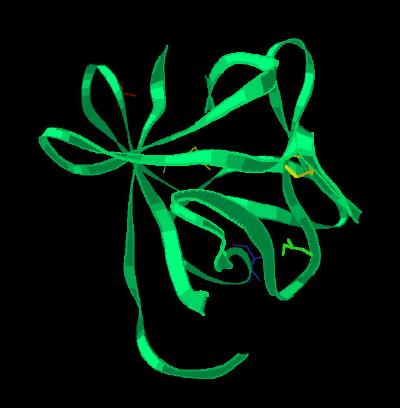 |
| Click on KiNG to see | Ribbon Rendering of FGF 19 |
Kinemage 3: Secondary Structure Cartoon of FGF 19
|
180 K |
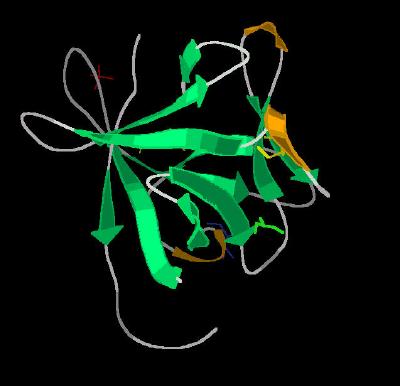 |
| Click on KiNG to see | Cartoon of FGF 19 |
Kinemage 4: FGF 19 Sulfate Ion Binding Site
The captured sulfate ion forms hydrogen bonds with the amide backbone of residues His-53, Leu-35, and Ser-56. Since this is in the region where the FGF ligand interacts with heparin and Domain 3 of the FGF receptors, this extended loop undoubtedly is a contributor to differences in physiological response of FGF 19 compared to FGF 1 and 2.
.
View 1 FGF 19
View 2 closer view of the sulfate binding site
| 184 K | 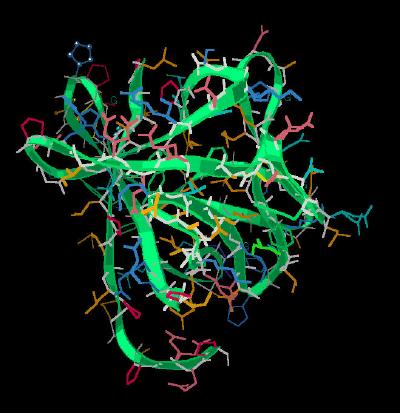 |
| Click on KiNG to see | FGF 19 Sulfate Ion Binding Site |
Kinemage 5: FGF 19 Superimposed Upon FGF 2
View 1 shows FGF 19 superimposed on the backbone of FGF 2
View 2 centers on the low affinity (discrimination) loop.
View 3 is looking directly into the heparin binding region (the "basic Canyon")
View 4 is centered on the N & C terminal junction
|
326 K |
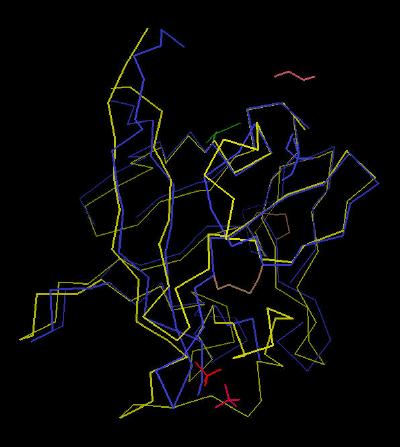 |
| Click on KiNG to see | FGF 19 Superimposed on FGF 2 |
Sequence: (X-Ray resolved residues 41- 176 of the rat FGF 19 sequence.)
Unresolved N-Terminal: GSMSGD
X-ray Resolved: PIRLRHLYTSGPHGLSSCFLRIRADGVVDCARGQSAHSLLEIKA
VALRTVAIKGVHSVRYLCMGADGKMQGLLQYSEEDCAFEEEIRPDGYNVYRSEKHRLPVSLS
Unresolved Loop 11: SAKQRQLYKNRGF
X-Ray Resolved: LPLSHFLPMLPMVPEEP
Unresolved C-Terminal: EDLRGHLESDMFSSPLETDS
Source:
The rat sequence was expressed in escherichia coli; Structural coordinates were taken from the Brookhaven Database file1PWA.
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences FGFR Sequences
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
Copyright 2005-2020 by Larry P. Taylor
Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute
University of Michigan
All Rights Reserved
Supported by the Pritzker Neuropsychiatric Disorders Research Consortium, and by NIH Grant 5 P01 MH42251, Conte Center Grant #L99MH60398, RO1 DA13386 and the Office of Naval Research (ONR) N00014-02-1-0879 to Huda Akil & Stanley J. Watson. at the Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute.