|
Human FGFR Isoform Sequence Alignments by Larry P. Taylor, Ph. D.
Feedback appreciated; please send comments to: Email: lpt Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute The University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI |
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences
This page: Alignments: FGFR 1 FGFR 2 FGFR 3 FGFR 4 FGFR 1-4
Trees: Tree 1 Tree 2 Tree 3 Tree 4 Tree 1-4
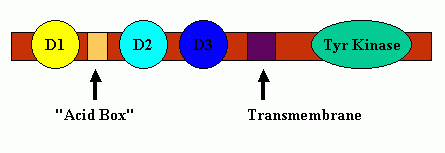
FGF receptors typically contain three Ig-like binding domains (with domains D2 and D3 being most involved in FGF-FGF receptor binding interactions), a short transmembrane spanning domain and a cytoplasmic component that possesses tyrosine kinase activity. Between receptor protein Domains D1 and D2 is a short span of acidic residues called the "Acid Box." A cartoon schematic of FGF Receptor Domains is shown below:

There are 4 major FGF receptors, but multiple splice variants, especially in exon III of the receptors (corresponding to FGF receptor protein domain D3) add to the complexity of the ligand-receptor binding event The third exon contains three parts: (IIIa, IIIb, and IIIc) and gene splicing events lead to D3 domain transcribed from the invariant IIIa portion of the gene followed by either b or c. This splice variation in the ligand binding domain defined by protein receptor domains D2 and D3 splits the four main receptors into a total of seven key human FGF receptors: FGFR 1b , FGFR 1c, FGFR 2b , FGFR 2c, FGFR 3b, FGFR 3c, and FGFR 4. The alternative splicing in D3 apparently is a tissue-specific process with isoform c associated with mesenchymal and isoform b predominate in epithelial cells.
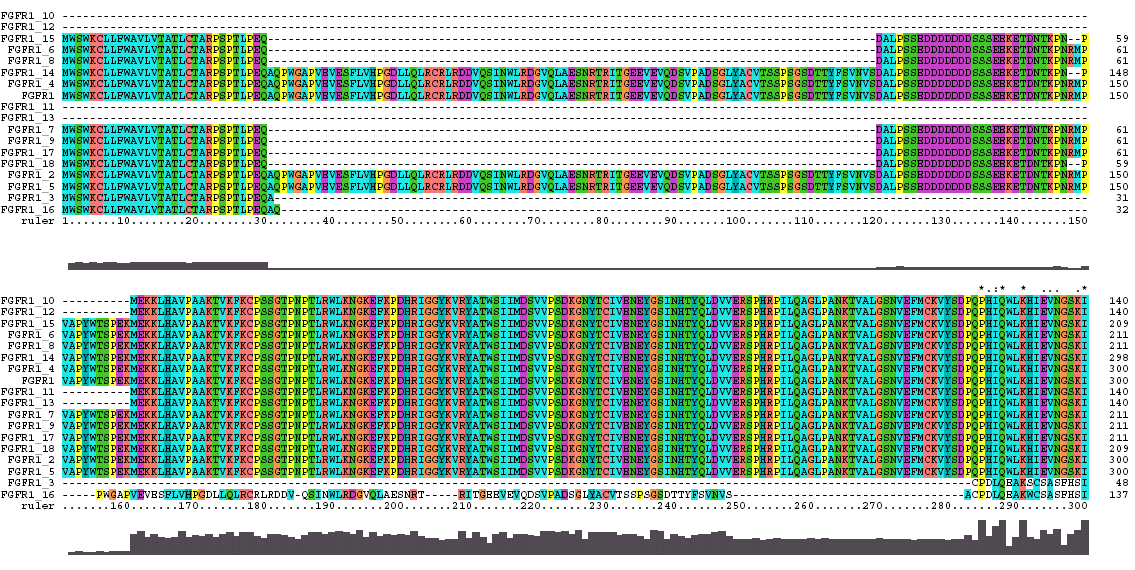
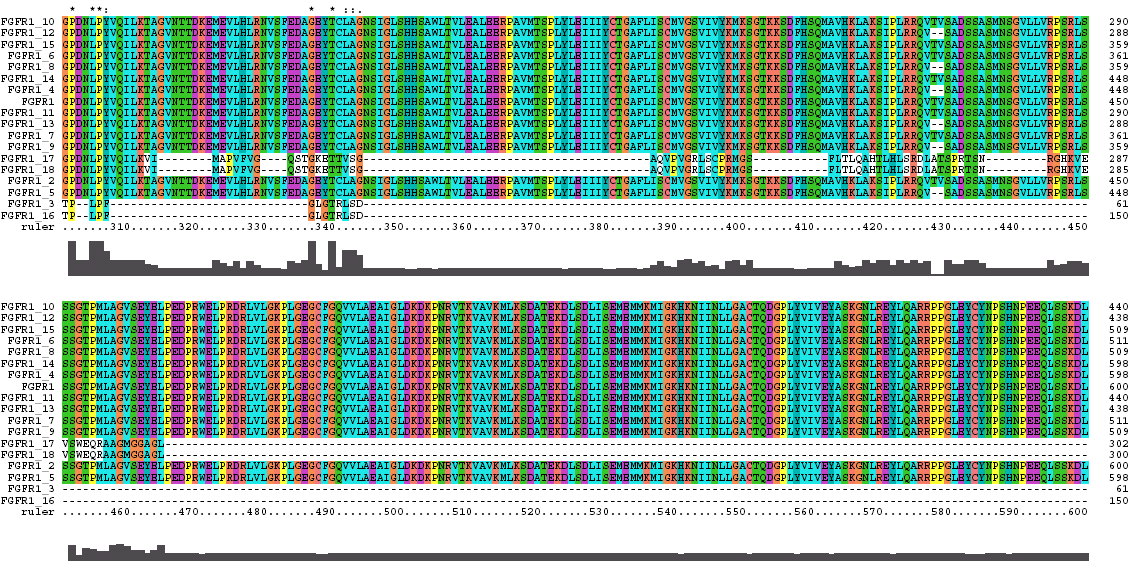
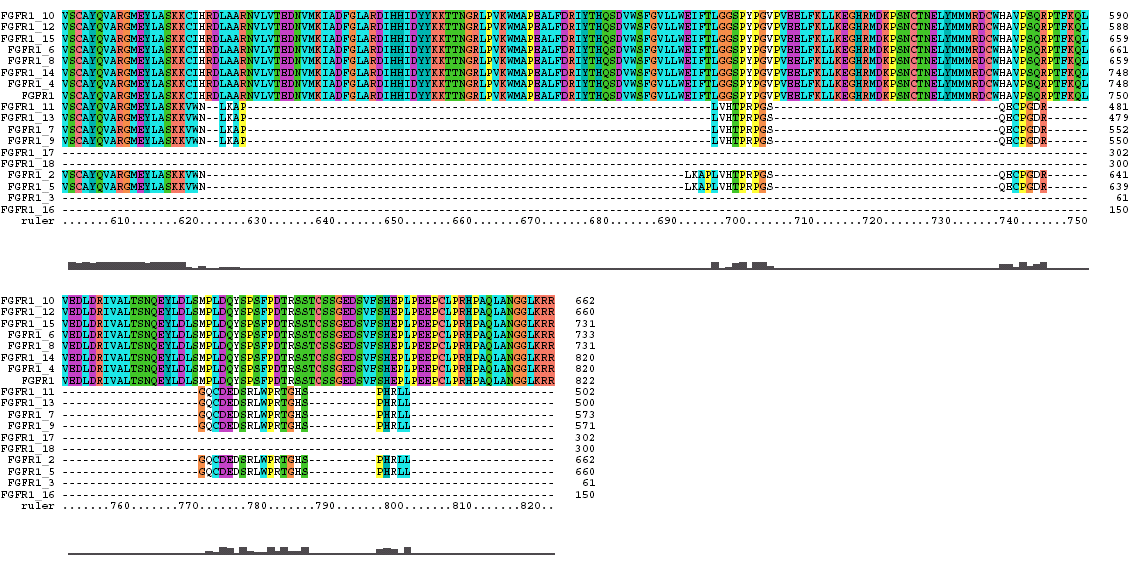
The amino acid sequences (FastA) for the human FGF receptors were downloaded from the appropriate NCBI Entrez entry and aligned with Clustal X.
Following each alignment is a table showing the sequence associated with the protein domains of the receptor.
At the end of this page is an explanation of the Clustal X Colors and Symbols.
The Clustal X Sequence Alignment for the Isoforms of FGFR 1 Precursor
|
FGFR 1 Domain |
Ruler Residues |
| IG 1 | 48-108 |
| Acid Box | 120-147 |
| IG 2 | 169-237 |
| IG 3 | 268-348 |
| Transmembrane | 375-397 |
| Tyrosine Kinase | 478-784 |
The Clustal X Sequence Alignment for the Isoforms of FGFR 2 Precursor
Isoform 5 is also known as receptor spice variant IIIc; isoform 18 is equivalent to splice variant receptor IIIb.
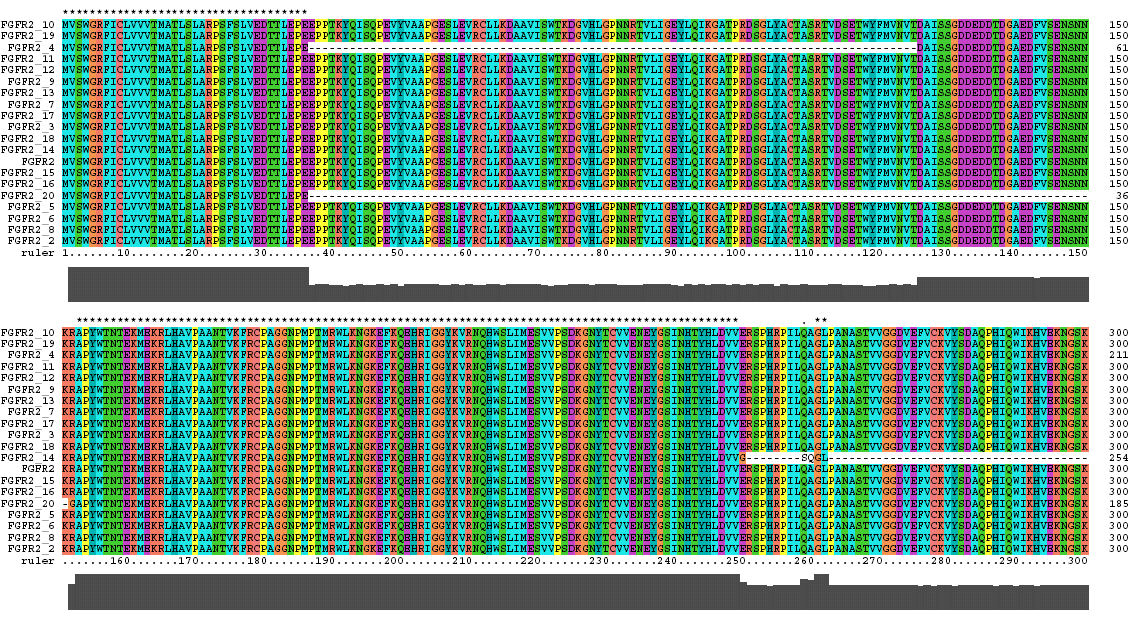
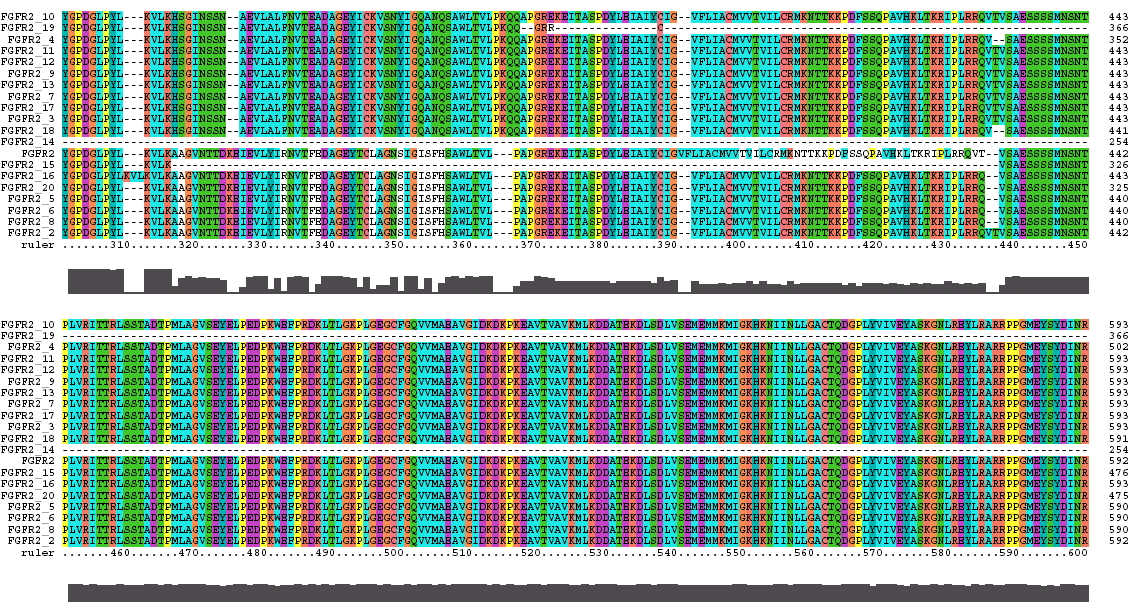
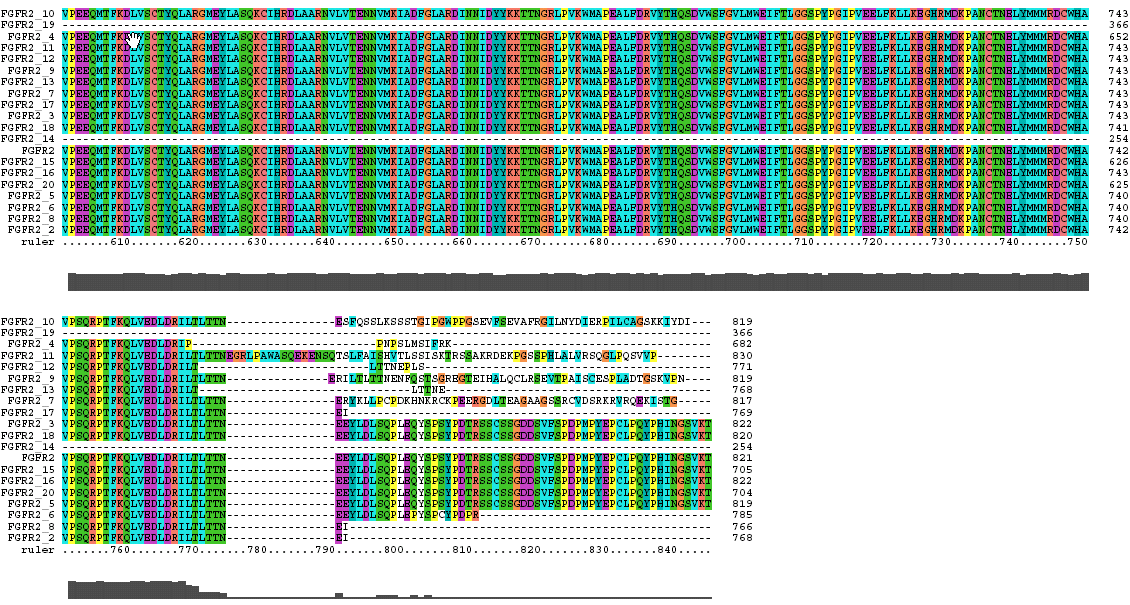
|
FGFR 2 Domain |
Ruler Residues |
| IG 1 | 53-114 |
| Acid Box | 126-142 |
| IG 2 | 170-238 |
| IG 3 | 269-352 |
| Transmembrane | 382-404 |
| Tyrosine Kinase | 490-766 |
The Clustal X Sequence Alignment for the Isoforms of FGFR 3 Precursor
Isoform 1 is also known as receptor spice variant IIIc; isoform 2 is equivalent to splice variant receptor IIIb.
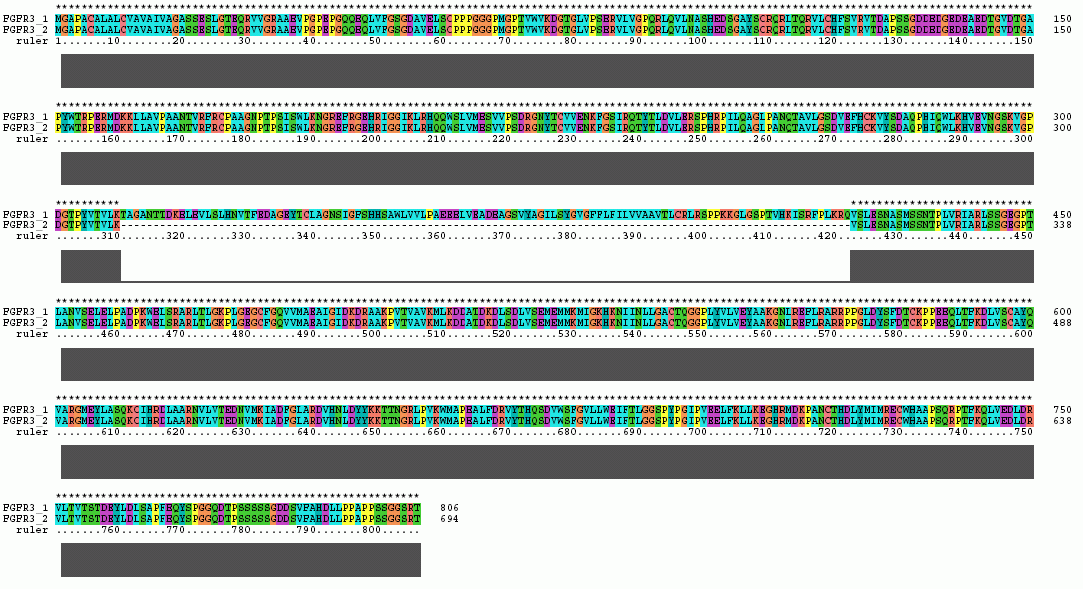
|
FGFR 3 Domain |
Ruler Residues |
| IG 1 | 52-126 |
| Acid Box | 138-148 |
| IG 2 | 167-235 |
| IG 3 | 266-346 |
| Transmembrane | 373-395 |
| Tyrosine Kinase | 472-748 |
The Clustal X Sequence Alignment for the Isoforms of FGFR 4 Precursor
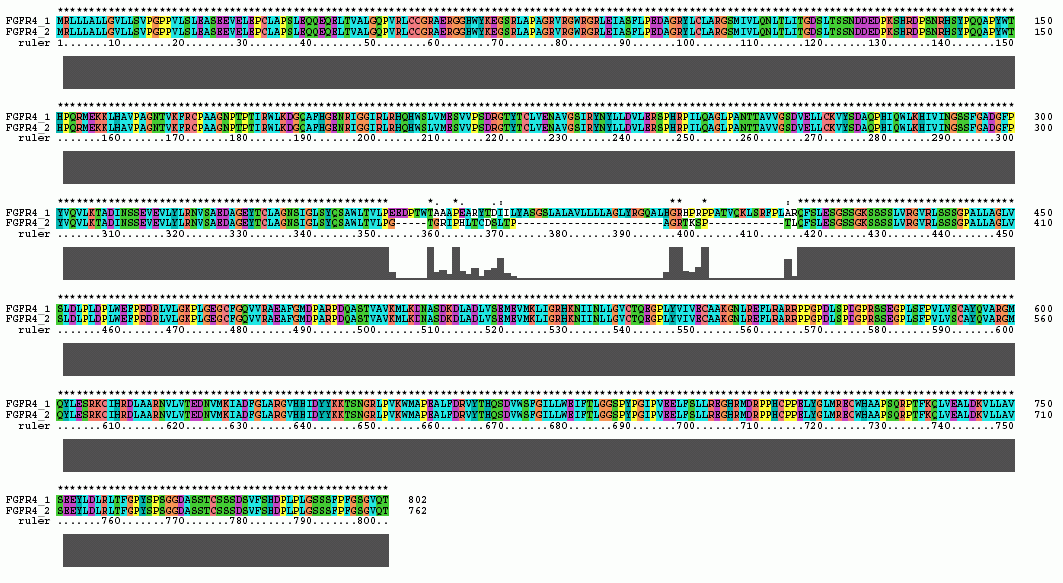
|
FGFR 4 Domain |
Ruler Residues |
| IG 1 | 48-108 |
| Acid Box | 126-135 |
| IG 2 | 163-231 |
| IG 3 | 262-340 |
| Transmembrane | 370-386 |
| Tyrosine Kinase | 467-743 |
The Clustal X Sequence Alignment for all the Isoforms of human FGFR 1-4
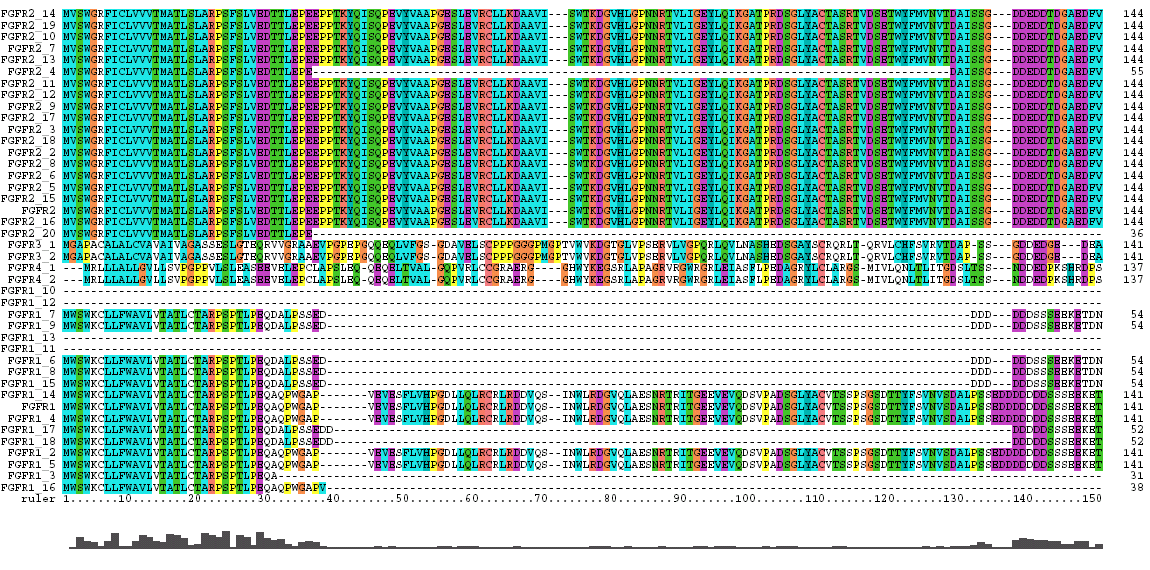
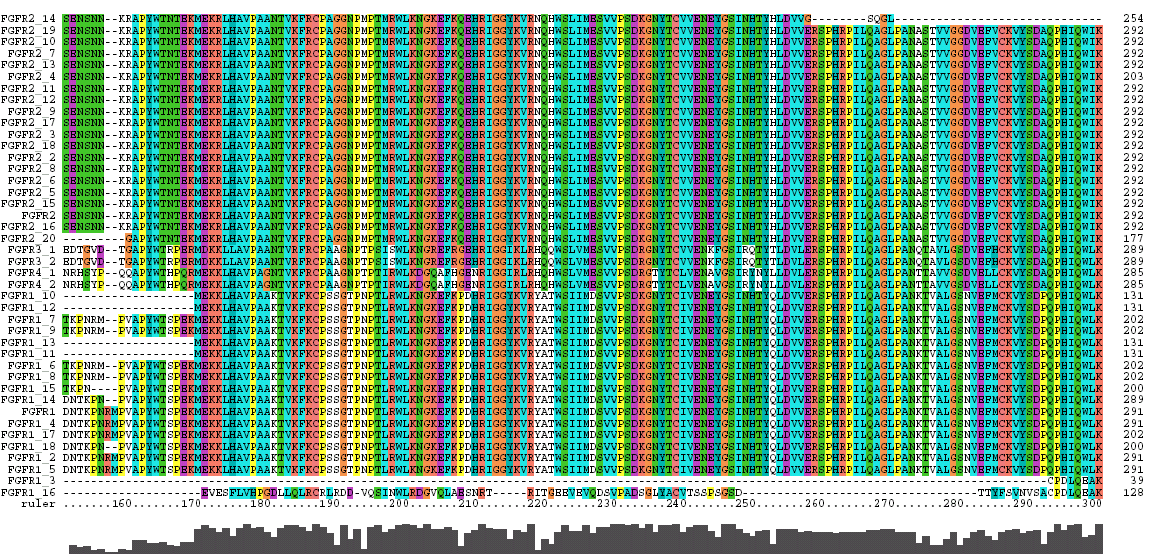
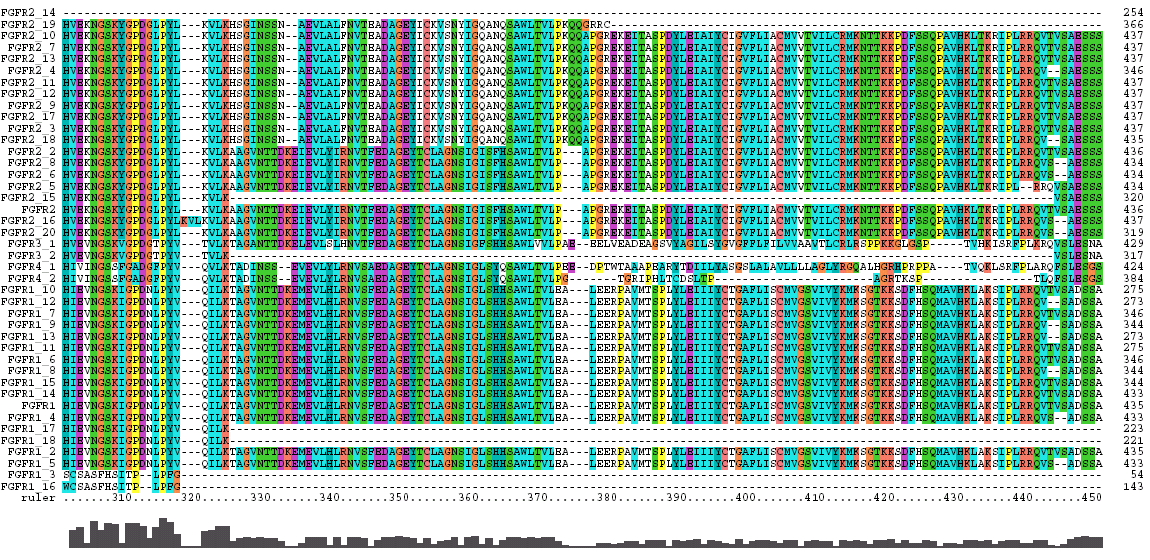


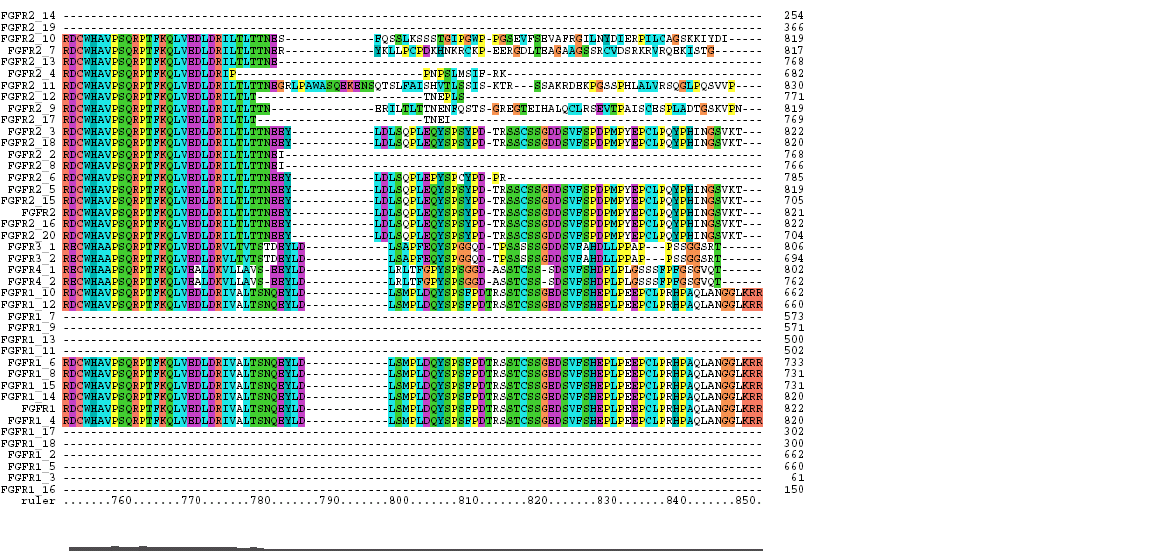
|
Domain |
Ruler Residues |
| IG 1 | 53-117 |
| Acid Box | 129-141 |
| IG 2 | 178-246 |
| IG 3 | 277-360 |
| Transmembrane | 389-411 |
| Tyrosine Kinase | 495-771 |
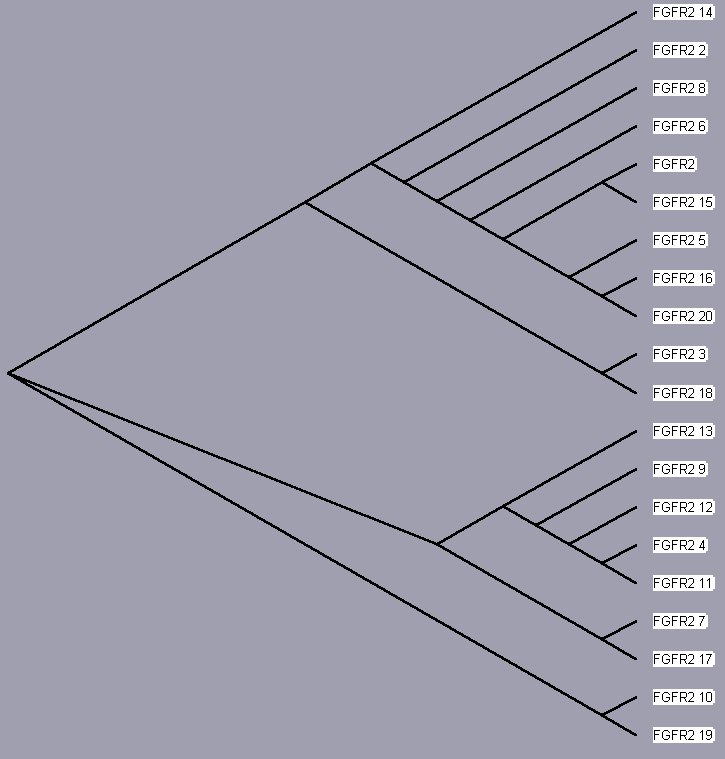
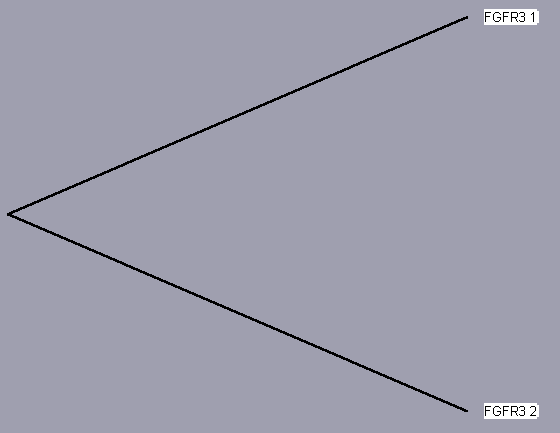
TreeView, based on the above sequence alignments, provides an evolutionary tree that attempts to trace each protein to a common ancestor protein. The trees for each receptor, even those of only 2 isoforms (for sake of completeness) are shown below. Since these proteins converge to a single hypothetical evolutionary ancestor, these FGFR proteins are homologous.
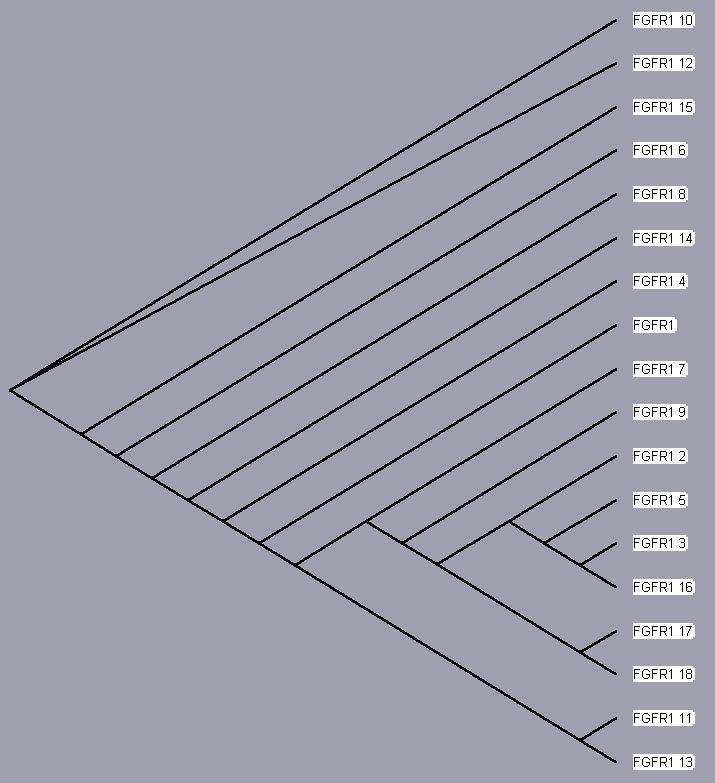
| FGFR 1 | UniProt | Entrez | iHOP | Protein Reference |
| FGFR 2 | UniProt | Entrez | iHOP | Protein Reference |
| FGFR 3 | UniProt | Entrez | iHOP | Protein Reference |
| FGFR 4 | UniProt | Entrez | iHOP | Protein Reference |
| FGFR 5 | UniProt | Entrez | iHOP | Protein Reference |
Clustal does a consensus analysis for each column in the alignment. Underneath the alignment is a plot for the quality of conservation; the higher the plot, the better than conservation at each position. In addition, above each column is a symbol denoting conservation type. The symbols are:
* indicates positions which have a single, fully conserved residue.
: indicates that one of the following 'strong' groups is fully conserved:
STA, NEQK, NHQK, NDEQ, QHRK, MILV, MILF, HY, FYW.
. indicates that one of the following 'weaker' groups is fully conserved: CSA, ATV, SAG, STNK, STPA, SGND, SNDEQK, NDEQHK, NEQHRK, FVLIM, HFY.
The coloring scheme for the amino acid residues is
Cyan = A, F, I, L, M, V, W (small, and/or hydrophobic)
Gray = H, Y
Green = N, Q, S, T (neutral & polar)
Magenta = D, E, R
Orange = G
Red = C, K
Yellow = P
This page: Alignments: FGFR 1 FGFR 2 FGFR 3 FGFR 4 FGFR 1-4
Trees: Tree 1 Tree 2 Tree 3 Tree 4 Tree 1- 4
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
Copyright 2005-2020 by Larry P. Taylor
Molecular &
Behavioral Neuroscience Institute
University of Michigan
All Rights Reserved
Supported by the Pritzker Neuropsychiatric Disorders Research Consortium, and by NIH Grant 5 P01 MH42251, Conte Center Grant #L99MH60398, RO1 DA13386 and the Office of Naval Research (ONR) N00014-02-1-0879 to Huda Akil & Stanley J. Watson. at the Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute.