<%@LANGUAGE="JAVASCRIPT" CODEPAGE="65001"%>
3D Simulation of Quantum Dot Growth
Conclusions and Recommendations
In this project, we present a three-dimensional finite element scheme to
simulate the growth process of quantum dots under both surface diffusion and
interface migration. Results include the nucleation process of QD from rough
surface, growth process in the early stage and also coarsening process. The
fourth-order Runge-Kutta method is used to improve the numerical stability.
Besides, the normalization of the governing equation also provides a tool to
study the effect of each free energy contributor.
Future works:
1. Consideration of anisotropic surface energy(3D) would lead to formation
of Pyramid-like QDs.

(http://www.hlphys.jku.at/groupsites/iv-vi/gallery/iv-vi_gallery.htm)
2. Consideration of wetting potential would lead to a wetting layer at the
initial stage of QD growth. [7]

Furthermore, it is also possible to design a pair of material which have
nonwetting interaction so that the deposited material could dewet the
substrate. This process could possibly cut the diffusion process between
neighbor islands, and stop the coarsening process at the late stage of
quantum dot growth. The dewetting process is an effective approach to
control the size of QDs.[8]

3. Pre-patterned substrate/multi-layered growth mode could be interesting
because the long-range order/positioning of the QDs are still major issues
for further application and commercialization.
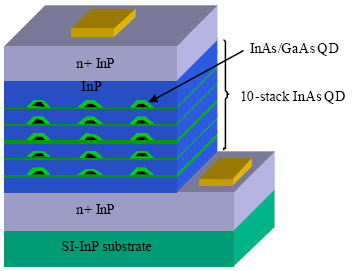

http://cqd.eecs.northwestern.edu/research/qdots.php
4. Our codes could only handle the small perturbation on the surface,
because the large interface movement requires update the Abaqus code to
refine the meshing in thickness.
5. We employ a CST (constant triangle element) as the element in this
project. It could be better to use a higher order element such as quadratic
rectangular element to improve the accuracy of the simulation.







