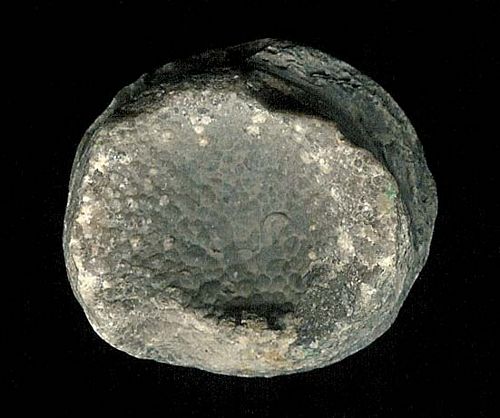
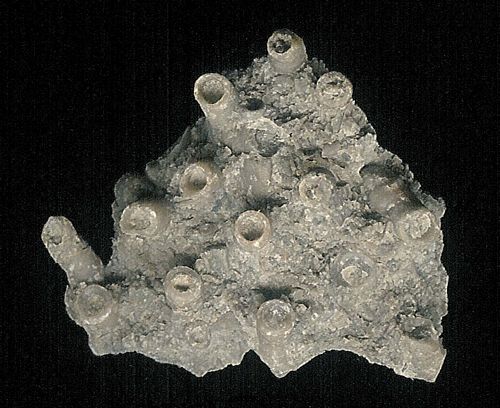
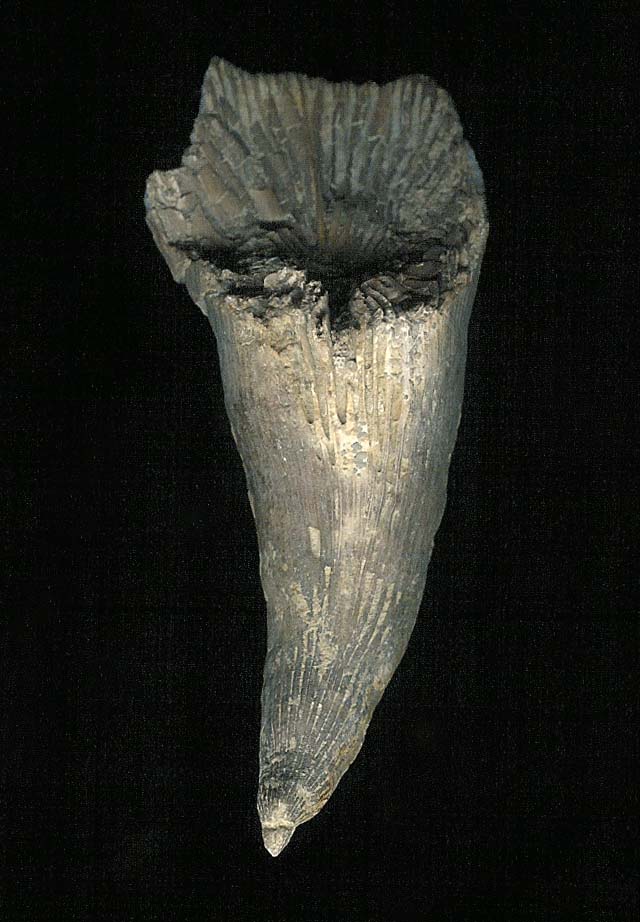
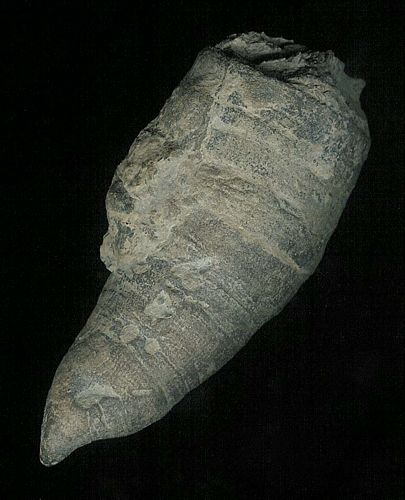
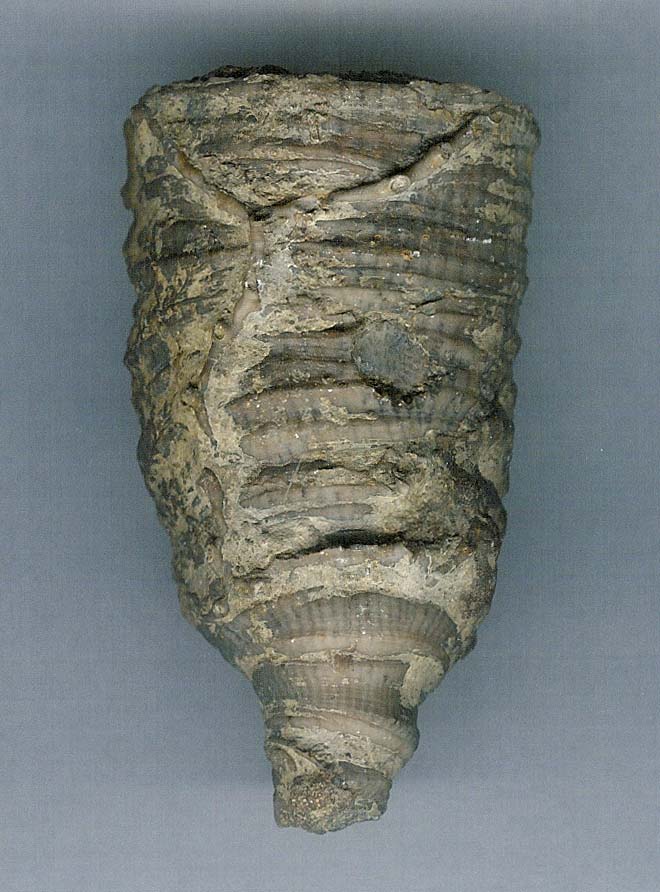
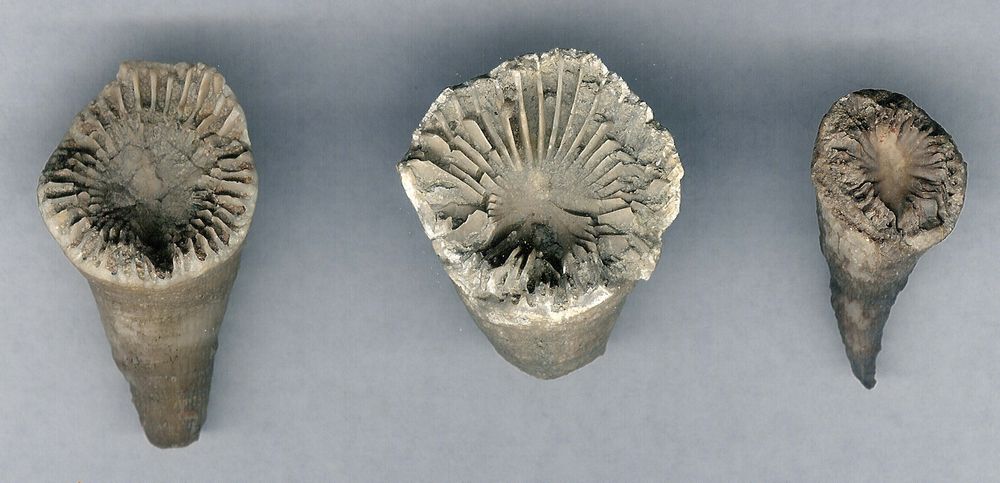
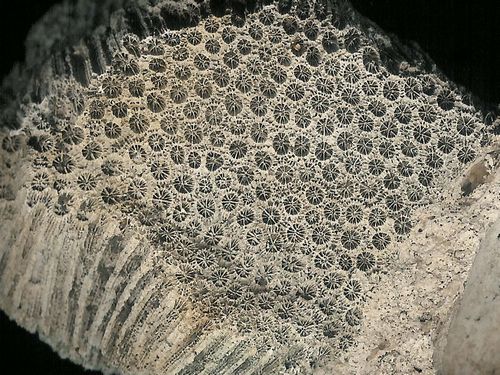
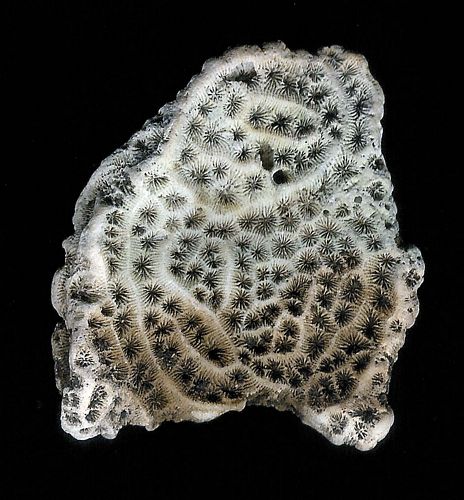
Fig. 7.
Halysites,
the ‘chain coral,’ Order Tabulata, Cambrian–Triassic; 516.0–232.0
million years, unchanged 284 million years. Contrary to Darwinism, which parades as science, the fossil record is not a record filled with mutating and morphing organisms. It consists of nothing but well-established
and successful organisms that survive for tens to hundreds of millions
of years. Read the dates in the figures. If you are intimidated by
propagandists, be they teachers, professors, school or university
officials into accepting buffoonery as fact, understand that they do
not know the fossil record beyond their template training, being
victims of the kind of education they are passing on to you or your children. When propagandists attempt to block people from conflicting ideas or evidence in the classroom, question their scientific integrity. Ask to see the trillions of fossilized
(not invisible) invertebrate morphs or to point to exact geographic
locations where purported evolutionary events have taken place. They
will not be able to do it.
|
|
|
an
end-all; the genetics fad is a simple trick raising analogy and
assumption to a level above the ‘chronologically recorded facts’ of the
fossil record—the only source of real-time non-analogical physical evidence regarding origins.
U.S.
children are now being trapped in science classrooms with template
instructors. This is because organizations which have lost scientific
integrity (e.g., AAAS) are participants in a far-reaching campaign to
control naïve and easily-duped legislators, judiciary, and educators. I
guarantee, none of those
people understand the fossil record. Otherwise, they would not allow
laws to pass that diminish students’ rights to study it objectively.
It
is harmful to the investigative spirit when an aggressive ideology
rules the science community. That community is currently after easy targets
such as children in school. At present, they have all their guns aimed
at religion. However, that leaves them wide open. They are in the
process of being taken at Aqaba and don’t even know it.
_________________
John
Feliks has specialized in the study of early human cognition for twenty
years demonstrating beyond any reasonable doubt that human cognition
does not evolve. Earlier, his focus was on the invertebrate fossil
record studying fossils in the field across the U.S. and parts of
Canada as well as studying many of the classic texts (Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology, Index Fossils of North America,
etc.). With the advent of the Next Generation Science Standards setting
up U.S. schools to force an ideology on children as fact while blocking
opposing evidence, Feliks encourages students to insist
that science teachers present all evidence objectively—like in normal
science. At present evolution is taught as propaganda with no rigor or
accountability.
|
Genus
|
Former living fossils
|
Range
|
Fossils recovered by the author
|
|
Disphyllidae/Cyathophylina
(coral families)
|
Unchanged
195 million years
Ordovician–Permian;
449.5–254.0 MYA
|
Worldwide |

1 3/4" (4.3 cm)
Hexagonaria; author; Devonian; Alpena, MI
|
Lithostrotionina
(rugosa colonial coral suborder)
|
Unchanged
185 million years
Ordovician–Permian;
449.5–265.0 MYA
|
Worldwide |

3 1/4" (8 cm)
Lithostrotion (Acrocyathus); Mississippian; Iuka, Mississippi
|
Cystiphyllida
(coral order)
|
Unchanged
184 million years
Ordovician–Permian;
456.1–272.5 MYA
|
Worldwide |
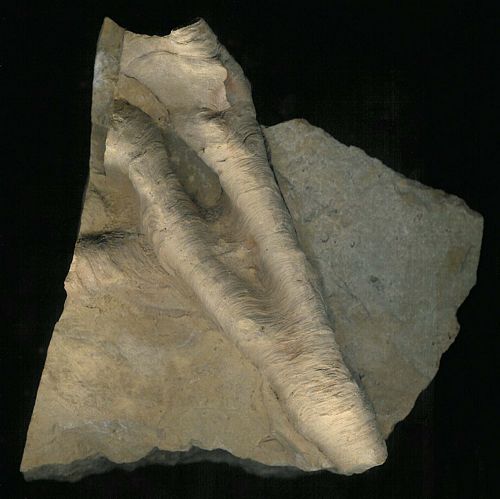
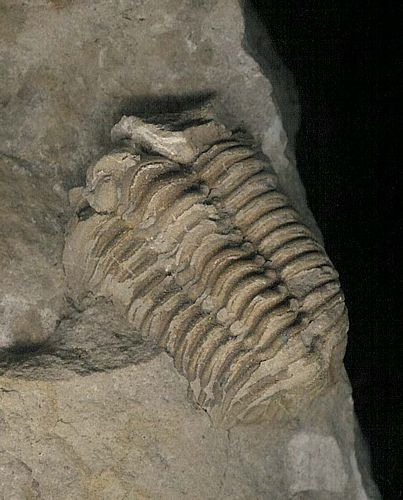
  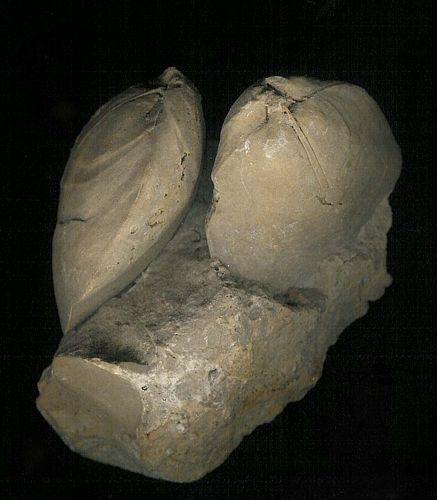
6 1/4" tall (15.8 cm)
Cystiphyllum;
Silurian; Phoneton, Ohio; found in context with Calymene (middle),
Pentameras (right), and Sphaeroxochus and Encrinurus trilobites
|
|
Alveolitina
(coral suborder)
|
Unchanged
182 million years
Ordovician–Jurassic;
436.0–254.0 MYA
|
Worldwide |

2" w. view (5 cm)
Alveolites rec. by author in situ Devonian; Arkona, Ontario
|
|
Unidentified large Rugose horn coral
|
Unchanged
162 million years
Ordovician–Carboniferous;
488.3–254.0 MYA
|
Worldwide |

3 3/4" tall (9.4 mm)
Large horn coral; Pennsylvanian; Junction City, Kansas
|
|
Lophophyllidiidae
(coral family) Note: Taxa date ranges can vary by a hundred million years and change daily like the stock market.
|
Unchanged
90 million years
Carboniferous–Permian;
342.8–252.3 MYA
|
Worldwide |
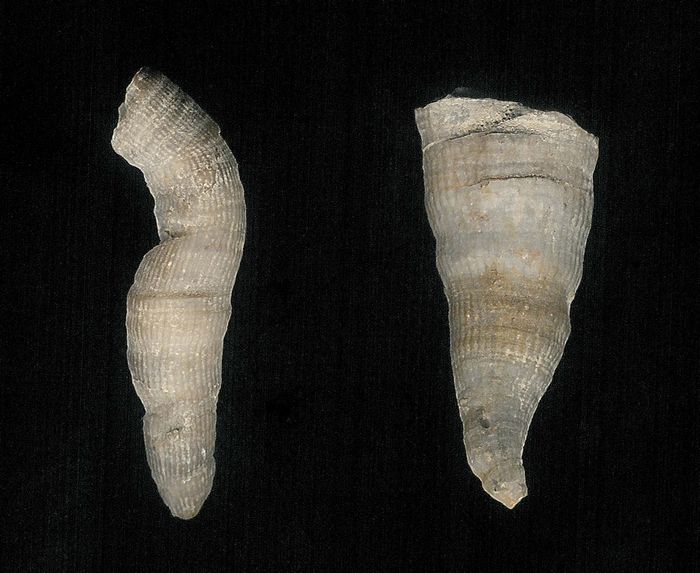

1 3/16" (3 cm)
Lophophyllidium westii & proliferum (1 1/6"); Pennsylvanian; Paris, Illinois
|
A few Paleozoic horn corals compared
The
idea is to start thinking “dog breeds” for all fossil types. Use of the
term ‘species’ has long been out of control in the fields of biology,
anthropology, and paleontology and can no longer be trusted as anything
more than a way to differentiate varieties. Remember, if
paleontologists never knew about modern-day dogs but found Chihuahua,
St. Bernard, and German Shepherd fossils they would call them different species. Anyone alive today knows that they are the same.
|
Unchanged
236 million years
Ordovician–Permian;
488.3–252.3 MYA
|
Worldwide |

 
2 11/16", 1", 1 1/16"
Left: Ordovician horn coral, Grewingkia, roadcut, Liberty, Indiana; Center: Devonian horn coral, Collinson Quarry, Milan, Illinois; Right: Pennsylvanian horn coral, Lophophyllidium, quarry behind St. Aloysius Church, Paris, Illinois
|
Fig. 6.
More examples of fossils with astounding existence ranges and no
morphing between genera. Instead of being coerced into Darwinism as
threatened by the NGSS, innocent school children need to be taught the
“facts” of the fossil record.
|
|
|