Steps of simulation
We restrict the simulation in a square cell of size 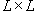 in the real space in the real space 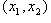 . The periodic boundary condition is applied to replicate the cell to the entire surface. The cell size must be large enough to contain sufficient numbers of features, but small enough to shorten the computation time. Linear perturbation analysis (Lu and Suo, 1999) estimates the equilibrium wavelength to be . The periodic boundary condition is applied to replicate the cell to the entire surface. The cell size must be large enough to contain sufficient numbers of features, but small enough to shorten the computation time. Linear perturbation analysis (Lu and Suo, 1999) estimates the equilibrium wavelength to be 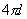 . In the simulation, we choose the cell size on the order . In the simulation, we choose the cell size on the order 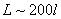 . The cell is divided into . The cell is divided into 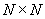 grids. The grid space, grids. The grid space, 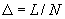 , should be small enough to describe the phase boundary. We choose , should be small enough to describe the phase boundary. We choose 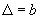 in our simulation. in our simulation.
The corresponding calculation cell in the reciprocal space 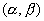 is of size is of size 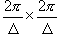 . The cell is also divided into . The cell is also divided into 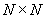 grids, with grid space grids, with grid space 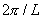 . The discrete Fourier transform connects the values of . The discrete Fourier transform connects the values of 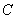 and and 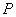 at the grid points in the real space to those of at the grid points in the real space to those of 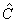 and and 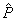 at the grid points in the reciprocal space. The Fast Fourier Transformation (FFT) is applied. at the grid points in the reciprocal space. The Fast Fourier Transformation (FFT) is applied.
The following figure is a schematic representation of the steps in the simulation. The input comprises the initial concentration distribution, as well as the parameters Q and 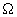 . At each time step, calculate . At each time step, calculate 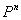 from from 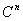 according to Eq. (20) at every grid point in the real space. Then apply the FFT and transform the values of according to Eq. (20) at every grid point in the real space. Then apply the FFT and transform the values of 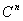 and and 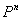 at all the grid points in the real space to those of at all the grid points in the real space to those of 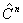 and and 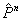 in the reciprocal space. Update to in the reciprocal space. Update to 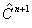 according to Eq. (24) at every grid point in the reciprocal space. Apply the inverse FFT to according to Eq. (24) at every grid point in the reciprocal space. Apply the inverse FFT to 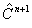 to obtain the concentration field to obtain the concentration field 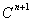 in the real space. Repeat the above procedure for the next time step. in the real space. Repeat the above procedure for the next time step.
|

