Nuclear fallout is the particles of matter in the air made radioactive from a nuclear explosion. Some of these particles fall in the immediate area and some get blown by upper winds many thousands of miles. Eventually they fall to the earth. This is called fallout.
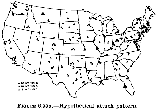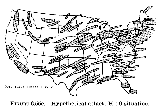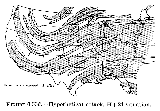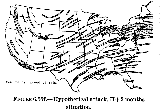 Simulation
of fallout in the US.
Simulation
of fallout in the US.
The rate of fallout largely depends on the altitude of the nuclear explotion and to a lesser
extent the magnitude of the explotion. If the explotion is in the air where it is unable to suck
dirt particles from the ground then the particles are lighter and take much longer to fallout.
If the blast is able to get particles from the ground then they fall much quicker in a more immediate
area.
Weather conditions can affect fallout immensely. Particularly rainfall can "rain out" fallout
to create very intense localized concentrations. This poses a serious health hazard.
Here is the effects of radiation on a humans.
Below 100 rems
No obvious sickness occurs. There might be a fluctuation in white blood cell count, and may cause
temporary male sterility.
100-200 rems
Mild symptoms occur. Blood and sperm forming tissues are affected. Mild nausea and vomiting might
occur. Temporary male sterility. Loss of appetite, fatigue might last up to 4 weeks.
200-400 rems
Illness becomes increasingly severe, and significant mortality sets in. Onset of initial symptoms
occur 1-6 hours and last 1-2 days. Nausea is universal and vomiting is 50% at 280 rems.
After this a 7-14 day latency period sets in. Initial symptoms reoccur and also might include
hair loss, fatigue, hemorrhage of the mouth, kidney. Susceptibility to infection is serious.
At 300 rems the possibility of mortality without medical treatment increases to 10%. Possibility of
permanent female sterility appears. Recovery takes around a month.
400-600 rems
Mortality rises steeply, from around 50% at 450 rems to 90% at 600 unless there is medical intervention.
The symptoms listed for 200-400 rems increase in occurrence and severity, reaching 100% occurrence
at 600 rems. When death occurs, it is usually 2-12 weeks after exposure and results from infection
and hemorrhage. Recovery takes several months to a year, blood cell counts may take even longer
to return to normal. Female sterility becomes probable.
600-1000 rems
Survival depends on stringent medical intervention. Bone marrow is almost completely destroyed and
will require a transfusion of the bone marrow. Death usually follows 1-4 weeks from infection and
internal bleeding. The recovery might never completely happen and if it does will take years.
Above 1000
Above 1000 will cause severe intestinal and metabolic problems which include severe diarrhea,
intestinal bleeding, and loss of fluids. Death will follow in a few hours from circulatory
collapse.
From 1000-5000 the onset time drops from 30 minutes to 5 minutes. Following the initial severe
nausia a period of apparent well-being will last a few hours to a few days often called the
walking ghost phase. The terminal phase will last 2-10 days. In rapid succession prostration,
diarrhea, anorexia, and fever follow. Death is certain, often preceded by delirium and coma.
Medical treatment is only to relieve suffering.
Above 5000 rems metabolic disruption is severe enough to interfere with the nervous system.
Immediate disorientation and coma will result, onset is within seconds to minutes. Convulsions
occur which may be controlled with sedation. Victim may linger for up to 48 hours before
dying.
The U.S. military assumes that 8000 rads of fast neutron radiation (from a neutron bomb) will
immediately and permanently incapacitate a person.
*These values are from exterior absorption. Interior would be 70% of these values to produce the same effect.
In Chernobyl the survival rates of the people in the 400-1000 rems range was actually higher then
what was given above.
To put in in perspective the average human receives 360 millirem (.360 rems) a year of radiation from naturally occurring isotopes.
Radiation has other effects. It can cause mutations. These mutations can either be somatic mutations (not inherited) or genetic mutations which are in reproductive cells and thus the mutations are passed on to offspring. Radiation also has long term effects on human health. It has been linked to leukemia, bone, lung, and breast cancer. It was thought at one time that radiation would cause nonspecific life shortening. There has been no evidence to suggest this anymore though.
It was also once believed that radiation would drastically effect aquatic animals such as fish. There have been a number of
experiments done on this. All have shown little effect of radiation on fish. Only in extreme cases where fish were exposed
to 11 rems a day was there any evidence of mutations and life shortening.
Radiation can stay resonant for many years. Here is the breakdown of the half-lives of the most common nucleotides.
| Radionuclide | Half-Life | Products of Fission | Half-Life | |
| Uranium-233 | 158,000 yrs | Iodine-131 | 8 days | |
| Uranium-235 | 704 Million yrs | Krypton-85 | 10.8 yrs | |
| Uranium-238 | 4.47 Billion yrs | Tritium | 12.3 yrs | |
| Thorium-232 | 14 Billion | Strontium-90 | 28 yrs | |
| Plutonium-239 | 24,400 yrs | Cesium-137 | 30 yrs |
It was observed that from 1963 to 1965 the annual dose of global fallout dropped 50%. And from 1965 to 1969 it dropped 60%.