Position Dependent Chemical Potential
In the previous calculations,  and and  (the chemical
potential of pure component B and A on the substrate) are assumed material
constants. However, when the substrate
is pre-patterned with some atoms, (the chemical
potential of pure component B and A on the substrate) are assumed material
constants. However, when the substrate
is pre-patterned with some atoms, 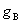 and and 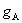 become
position dependent. The
following figure demonstrates the idea. When an A-atom is deposited on different regions of the substrate, it
is attached to a local surface composed of different kinds of materials. The A atom interacts with different
surface atoms and hence causes become
position dependent. The
following figure demonstrates the idea. When an A-atom is deposited on different regions of the substrate, it
is attached to a local surface composed of different kinds of materials. The A atom interacts with different
surface atoms and hence causes 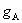 to be spatial
dependent. to be spatial
dependent.
It is found only  enters the diffusion
equation. enters the diffusion
equation.
Define  . .
It is also found
the difference of  at various
positions, rather than the value of at various
positions, rather than the value of 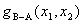 , influences the diffusion. , influences the diffusion.
In following
calculation, 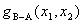 is
given a spatial function that looks like the following figure. In the blue region, is
given a spatial function that looks like the following figure. In the blue region, 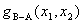 is
assumed 0.1, in other regions is
assumed 0.1, in other regions  is assumed 0. is assumed 0.
In following sequence,
all the other parameters are the same as previous calculations with isotropic
surface stress for average concentration 0.4.
(The average
concentration is taken to be 0.4. The initial condition is set to
fluctuate randomly within 0.001 from the average. The time unit in the figures is t.
The size of each figure is 256b´256b. In the simulation, W and Q are taken to be 2.2 and
1, respectively)
During the
evolution, the six pre-patterned lines attract A atoms and repel B atoms. Ordered lattice of dots formed within
each small cell defined by the pre-patterned lines.
t=0 |

|
t=10 |

|
t=100 |

|
t=500 |

|
t=1000 |
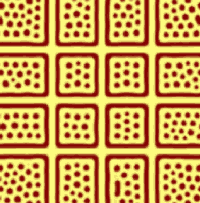
|
t=1.0E4 |

|
|

