|
by Larry P. Taylor, Ph. D.
Feedback appreciated; please send comments to: Email: lpt Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute The University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI |
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences FGFR Sequences
This Page: Helical Wheel Surface Potential Modeling Kinemages
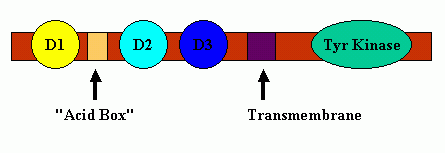
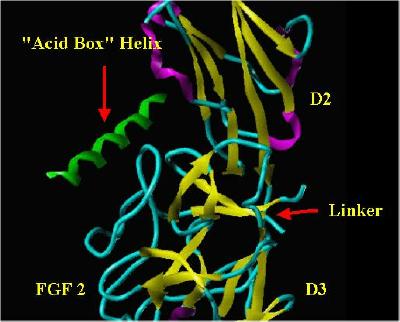
The FGF receptors typically contain three Ig-like binding domains (with domains D2 and D3 being most involved in FGF-FGF receptor binding interactions), a short transmembrane spanning domain and a cytoplasmic component that possesses tyrosine kinase activity. Between receptor protein Domains D1 and D2 is a short span of acidic residues called the "acid box." A cartoon schematic of FGF Receptor Domains is shown below:
FGF Receptor Domains.

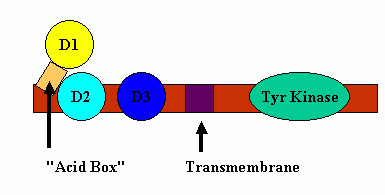
The D1 and the linker region between D1-D2 have much sequence variability, multiple splice variants, are structurally disordered (even in the presence of bound FGF ligand), and are considered not necessary for ligand binding ( FGF binds to FGFR even in the total absence of protein receptor domain D1). It is hypothesized that the "acid box" can participate in the regulation of FGF binding to FGFR's in that the multiple acidic sites of the "acid box" can mimic the negative potential surface of heparin-like compounds and thus, bind at the heparin-binding sites located on the surface of the D2 region of the FGF receptor without initiating a biological response (an auto-inhibition mechanism). A cartoon of this inhibition is shown below:
"Acid Box" Mediated Auto-Inhibition
For this auto-inhibition to occur, the "acid box" should resemble the 3-dimensional charge distribution found in heparin. The amino acid sequence in the "acid box" region of the human FGFR 2 receptor has the following sequence. DAISSGDDEDDTEGAED. This sequence is predicted (Chou-Fasman) to assume a helical conformation. The snake representation and helical wheel for this "acid box" sequence are shown below:
The SYBYL stick representation of this sequence represented as a helix is shown below:
The "Acid Box"
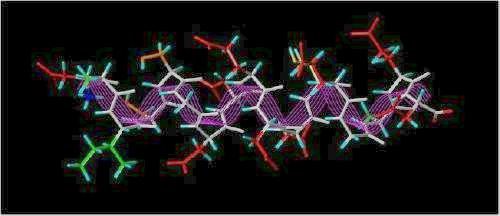
(colors: Hydrophobic = green; Hydrophilic = orange; Acidic = red; Hydrogen atoms = cyan; white backbone traced with magenta lines)
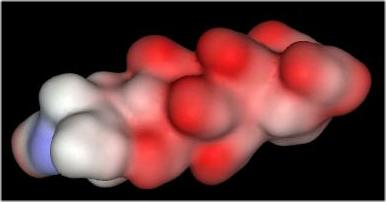
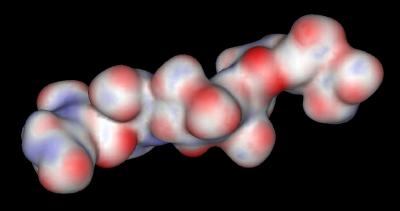
The distribution of negative charges (from sulfate and carboxylate groups) in Heparin form a negative charge potential that lines the ridge of the Heparin helix such that a negative center (red color) is found every 17-19 angstroms The surface potential of the "acid box" sequence and Heparin are shown below:
|
"Acid Box" |
Heparin |
 |
 |
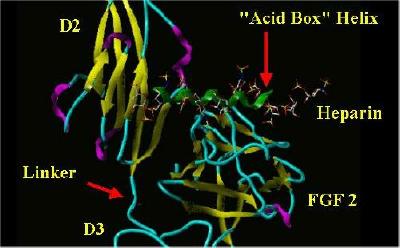
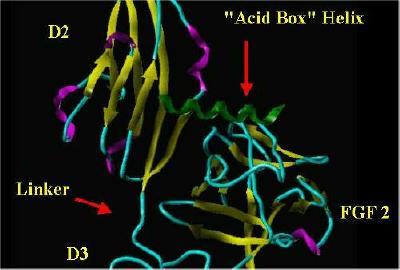
The "acid Box" helix was manually placed in the same space as Heparin in a monomer from the FGF 2-FGFR 1-Heparin 2;2;2 complex. The SYBYL rendering of this is shown below:
"Acid Box" In Heparin's Space
 |
 |
|
"Acid Box" superimposed over Heparin |
"Alpha Box" helix Only |
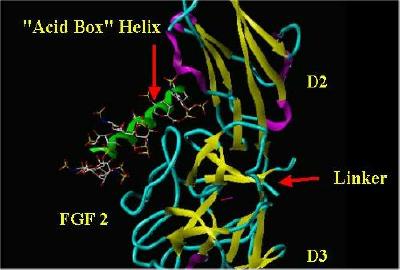
Another angle of the same situation:
 |
 |
|
"Acid Box" superimposed over Heparin |
"Alpha Box" helix Only |
Since the "acid box" can fit into the space surrounding the heparin-binding surface of the D2 Domain for the FGF receptor, it seems reasonable that the "acid box" could restrict access to the D2 Domain by either incoming FGF and/or Heparin molecules.
The real-time visualization using KiNG of the structures on this site requires a java-enabled (JRE from Java) browser.
Possible Icons to the left of molecular model image on the download page
| Java Not Activated | Java Not Activated | Java Functional |
 |
Blank Area
or message: Image requires a Java enabled browser
|
 |
| KiNG Inactive | KiNG Inactive | KiNG Full Functional |
A single click on the KiNG logo will launch the appropriate kinemage.
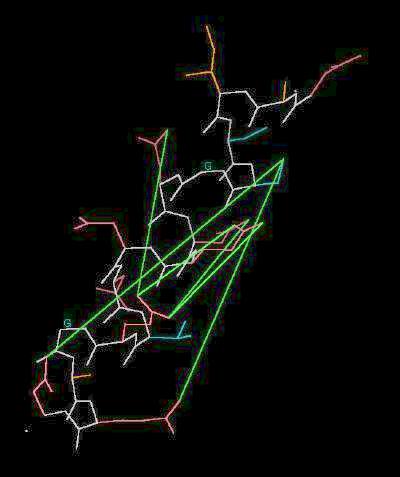
Kinemage 1: The Acid Box
Selected distances between negative sites are indicated with green lines
|
28 K |
 |
| Click On KiNG to see |
"Acid Box" |
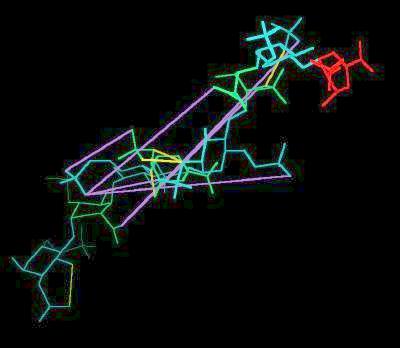
Kinemage 2: Heparin
Selected distances between negative sites are indicated with lilac lines
|
16 K |
 |
| Click On KiNG to see |
Heparin |
Since the distribution of negative charges (from sulfate and carboxylate groups) in heparin is similar to charge distribution in the "acid box," it is reasonable to assume the "acid box" sequence can mimic heparin.
Sequence: (FGFR 2 "Acid Box")
DAISSGDDEDDTEGAED
Sources:
Heparin was extracted (using SYBYL) from Brookhaven Database File 1FQ9 (Chain E). The "Acid Box" was built in SYBYL and energy minimized (SYBYL Minimization Energy = -187.760 kcal/mole) using the Kollman All-Atom force field with charge considerations. The surface potentials were generated using the Windows version of AccelyrSys Viewer Lite.
This Page: Intro Helical Wheel Surface Potential Modeling Kinemages
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences FGFR Sequences
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
Copyright 2006-2020 by Larry P. Taylor
Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute
The University of Michigan
All Rights Reserved
Supported by the Pritzker Neuropsychiatric Disorders Research Consortium, and by NIH Grant 5 P01 MH42251, Conte Center Grant #L99MH60398, RO1 DA13386 and the Office of Naval Research (ONR) N00014-02-1-0879 to Huda Akil & Stanley J. Watson. at the Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute.