 |
 |
|
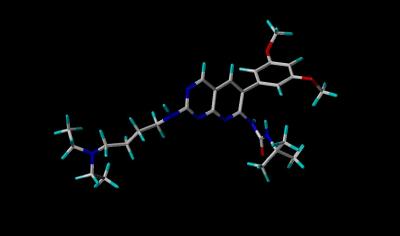
Stick View of PD-173074 |
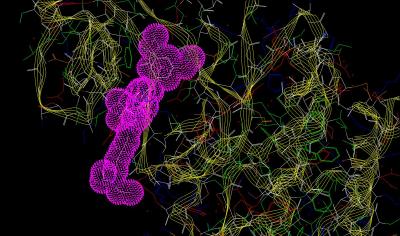
Inhibitor Surface Resembles a Famous Rodent |
|
Inhibitor PD-173074 Bound to the Tyrosine Kinase Domain of FGFR 1 by Larry P. Taylor, Ph. D.
Feedback appreciated; please send comments to: Email: lpt Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute The University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI |
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences FGFR Sequences
Inhibitor PD-173074 Bound to the Tyrosine Kinase Domain of FGFR 1
Most FGF receptors contain a tyrosine kinase motif downstream from the ligand binding domain and membrane spanning region. Since FGF is implicated in a variety of growth disorders and cancers, it seems reasonable that blocking the FGF signal activity via inhibition of the tyrosine activity would be of therapeutic value. So, there is currently a search for good inhibitors of this system.
The crystal structure (Kinemage 1) is from an engineered protein that represents residues 404-761 (sequence below) of the human FGF receptor 1 (FGFR 1). The ribbon rendering of the inhibitor-receptor complex is shown in Kinemage 2. The inhibitor, PD-173074, resides in the ATP binding cleft which occurs between two distinctly different structural clusters that are characteristic of tyrosine kinase activity. (This is easiest to visualize in Kinemage 3.) The characteristics of the unit cell for this structure are summarized at pdbsum. The SYBYL stick rendering of the inhibitor PD-173074 and the surface contour of the inhibitor when bound to Tyrosine Kinase Domain of FGFR 1 are shown below.
 |
 |
|
Stick View of PD-173074 |
Inhibitor Surface Resembles a Famous Rodent |
|
Atom |
Color |
Structure |
Color |
|
|
Carbon |
white |
Peptide Backbone |
yellow lines |
|
|
Hydrogen |
cyan |
Inhibitor Surface |
magenta dots |
|
|
Oxygen |
red |
|||
|
Nitrogen |
blue |
Kinemage 4 highlights the residues that
interact with the inhibitor within the binding cleft.
Within the ATP cleft, the pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine ring system makes hydrophobic contact with FGFR 1 residues
Leu-484, Ala-512, Tyr-563, Ala-564, and Leu-630. There are ligand-receptor hydrogen bonds from pyrimidine N3 to the amide hydrogen of
Ala-564 and from the butylamino nitrogen to carbonyl of Ala-254. In addition, one
methoxy group oxygen is hydrogen bonded to
Asp-641. This Asp is at the beginning of the Asp-Phe-Gly "triad" that signifies the beginning of the protein kinase activation loop.
The ligand forms an internal hydrogen bond from the urea group to N8 of the ring system via an ordered water molecule
(see Kinemage
4, view 5).
Comparison of unbound and PD-173074-bound tyrosine kinase motif of FGFR 1 shows nearly total conservation of structure. The distinct exception is
Lys-514 which has moved to provide more ligand access to the binding cleft. A
comparison of the bound vs. unbound Lys-514 position can be seen on the Tyrosine
Kinase Comparison page (Kinemage 3, View 5).
The methoxy groups make contacts with receptor residues Lys-514, Glu-531,
Met-535, Ile-545, Val-559, Val-561, Ala-640 and Phe-642.
The total surface area buried by inhibitor PD-173074 binding to the tyrosine kinase cleft of FGFR 1 is a rather respectable 1033
A3 .
The Kinemages:
The real-time visualization using KiNG of the structures on this site requires a java-enabled (JRE from Java) browser.
Possible Icons to the left of molecular model image on the download page
| Java Not Activated | Java Not Activated | Java Functional |
 |
Blank Area
or message: Image requires a Java enabled browser
|
 |
| KiNG Inactive | KiNG Inactive | KiNG Full Functional |
A single click on the KiNG logo will launch the appropriate kinemage.
Kinemage 1: The Crystal Dimer FGFR 1 Bound To the Inhibitor PD-173074
View 1 the unit cell
View 2 ordered water (number 190) that is present only in chain B
of the crystal. This water molecule is associated with simultaneous intra-receptor and intra-ligand hydrogen bonding (see kinemage 4, view 5).
|
42 K |
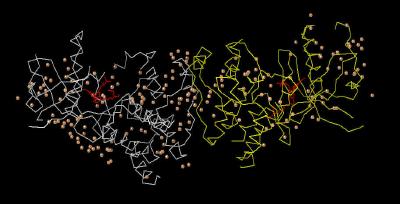 |
| Click on KiNG to see | Unit Cell of PD-173074 Bound to FGFR 1 |
Kinemage 2: Inhibitor PD-173074 Bound to the Monomer Unit (Chain A) of FGFR
1
View 1 monomer complex of FGF1 with PD-173074
View 2 closer view of the binding cavity.
|
385 K |
 |
| Click on KiNG to see | PD-173074 Bound to FGFR 1 |
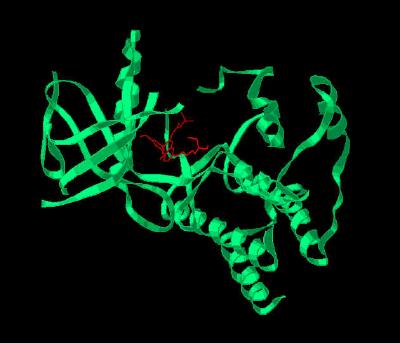
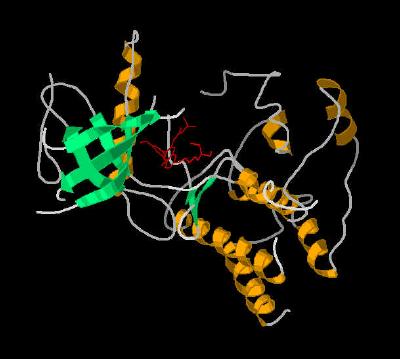
Kinemage 3: A Secondary Structure Cartoon of FGFR 1 Bound To the Inhibitor
PD-173074
View 1 monomer complex of FGF1 with PD-173074
View 2 closer "face-on" view of the binding cavity.
View 3 "top" view of the binding cavity.
Note the ATP binding cleft resides between two separate secondary structure clusters ... one primarily alpha helix and the other primarily beta sheet.
|
303 K |
 |
| Click on KiNG to see | Cartoon of PD-173074 Bound to FGFR 1 |
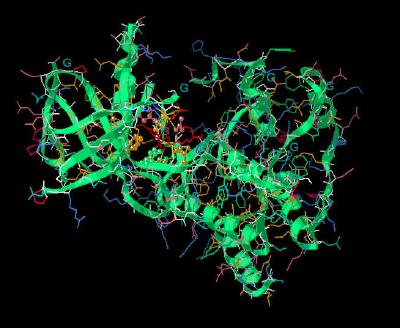
Kinemage 4: Residues of FGFR 1 Interacting with PD-173074
Within the ATP cleft, the pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine ring system makes hydrophobic contact with FGFR 1 residues Leu-484, Ala-512, Tyr-563, Ala-564, and Leu-630. There are ligand-receptor hydrogen bonds from pyrimidine N3 to the amide hydrogen of Ala-564 and from the butylamino nitrogen to carbonyl of Ala-254. In addition, one methoxy group oxygen is hydrogen bonded to Asp-641. This Asp is at the beginning of the Asp-Phe-Gly "triad" that signifies the beginning of the protein kinase activation loop.
There is an ordered water that interacts with receptor residues Lys-514 and Asp-641, as well as the inhibitor. This water is only resolved in the beta chain of the unit cell. For purposes of illustration, this ordered water has been added in an approximately equivalent position in chain A of this kinemage.
View 1 monomer complex of FGF1 with PD-173074
View 2 the binding pocket.
View 3 hydrophobic residues Leu-484, Ala-512, Tyr-563, Ala-564, and
Leu-630 that surround the pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidene ring system of the inhibitor
PD-173074.
View 4 the "triad," Asp-Phe-Gly (residues 641-643), associated with tyrosine kinase activity.
View 5 Lys-514 residue, which alters position on inhibitor binding.
View 6 the contact points of the phenyl-methoxy groups of the ligand with the receptor.
|
389 K |
 |
| Click on KiNG to see | Residues of FGFR 1 Interacting with PD-173074 |
The "fit" between PD-173074 and the ATP-binding region of the tyrosine kinase domain of FGF 1 is exceptional and accounts for its ability to inhibit tyrosine kinase activity of this receptor.
Sequence: (X-ray resolved residues are 465-762 of the human FGFR 1)
Unresolved N-Terminal: MVAGVSEYE
X-Ray Resolved: LPEDPRWELPRDRLVLGKPLGEGAFGQVVLAEAIGLDKDKP
NRVTKVAVKMLKSDATEKDLSDLISEMEMMKMIGKHKNIINLLGACTQDGPLYVIVE
YASKGNLREYLQARRPPGLEYSYNPSHNPEEQLSSKDLVSCAYQVARGMEYLASKK
CIHRDLAARNVLVTEDNVMKIADFGLARDIHHIDYYKKTTNGRLPVKWMAPEALFDR
IYTHQSDVWSFGVLLWEIFTLGGSPYPGVPVEELFKLLKEGHRMDKPSNCTNELYMM
MRDCWHAVPSQRPTFKQLVEDLDRIVALTS
Unresolved C-Terminal: NQE
Source:
Human sequence expressed in spodoptera frugiperda insect cell line sf9; Structural coordinates were taken from the Brookhaven Database file 2FGI.
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences FGFR Sequences
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
Copyright 2005-2020 by Larry P. Taylor
Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute
University of Michigan
All Rights Reserved
Supported by the Pritzker Neuropsychiatric Disorders Research Consortium, and by NIH Grant 5 P01 MH42251, Conte Center Grant #L99MH60398, RO1 DA13386 and the Office of Naval Research (ONR) N00014-02-1-0879 to Huda Akil & Stanley J. Watson. at the Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute.