 |
 |
|
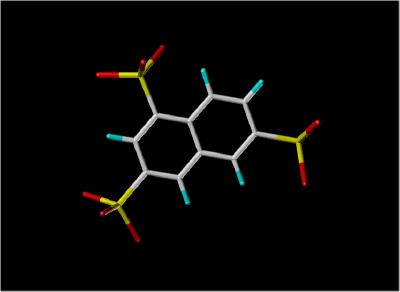
Stick View of NTS |
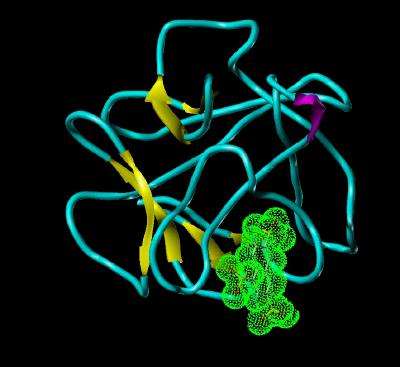
NTS Bound To FGF 1 |
|
by Larry P. Taylor, Ph. D.
Feedback appreciated; please send comments to: Email: lpt Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute The University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI |
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences FGFR Sequences
1,3,6-Naphthalene Trisulphonate (NTS) Bound To Acidic FGF (FGF 1)
Since FGF molecules are involved in tumor proliferation, one possible therapeutic approach would be to block the binding of FGF to heparin, thus preventing the formation of the FGF-heparin-FGF Receptor complex. The inhibitor of FGF activity, 1,3,6-naphthalene trisulphonate, appears to function in this manner since it binds to FGF 1 in the region
(the "basic canyon" ) of FGF known to bind heparin. The NTS to FGF 1 binding is competitive with heparin.
 |
 |
|
Stick View of NTS |
NTS Bound To FGF 1 |
| Atom | Color |
Structure |
Color | |
| Carbon | white | alpha | magenta | |
| Hydrogen | cyan | beta | yellow | |
| Oxygen | red | coil | cyan | |
| Sulfur | yellow | NTS surface | green dots |
Since the ligand-receptor complex would not crystallize, the ligand bound structure was determined using 2 dimensional nmr. Since the N-terminal region is susceptible to enzymatic degradation during isolation and purification, a core component (132 residues) was used. It has previously been shown that the 132 amino acid core maintains the same biological activity as the full 154 amino acid gene sequence for FGF 1.
Exchange rate studies for the peptide backbone amide protons suggest that the ligand-bound structure is fairly flexible. This may account for the inability of the ligand-receptor complex to form good crystals needed for X-Ray Diffraction studies.
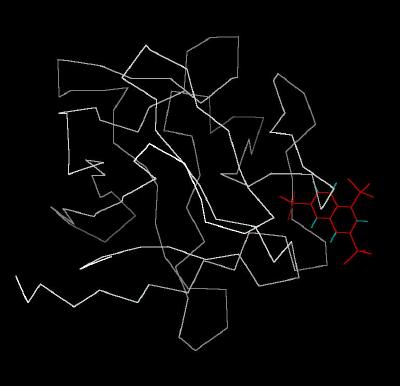
The Calpha trace of the inhibitor bound to FGF 1 is shown in Kinemage
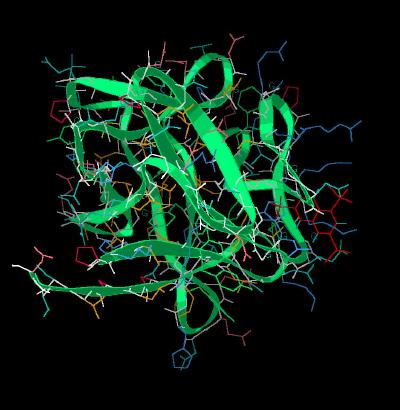
1. The ribbon rendering for this complex is shown in Kinemage
2. The characteristics of the unit cell for this structure are summarized at
pdbsum.
The nmr indicates that the sulfate groups of NTS interact with two Lysine residues (127 and 142).
These residues are highlighted in Kinemage 3.
An overlap of FGF 1 bound to heparin and FGF 1 bound to NTS (with FGF 2 as reference template) shows a distortion of FGF in the vicinity of the heparin binding region. It is clear that
NTS is occupying some of the same volume used by heparin (Kinemage
4).
The Kinemages:
The real-time visualization using KiNG of the structures on this site requires a java-enabled (JRE from Java) browser.
Possible Icons to the left of molecular model image on the download page
| Java Not Activated | Java Not Activated | Java Functional |
 |
Blank Area
or message: Image requires a Java enabled browser
|
 |
| KiNG Inactive | KiNG Inactive | KiNG Full Functional |
A single click on the KiNG logo will launch the appropriate kinemage.
Kinemage 1: Classic Kinemage of NTS Bound To FGF 1
|
10 K |
 |
| Click on KiNG to see | NTS Bound to FGF 1 |
Kinemage 2: Ribbon Rendering of the Inhibitor NTS Bound to FGF
1
|
204 K |
 |
| Click on KiNG to see | NTS Bound to FGF 1 |
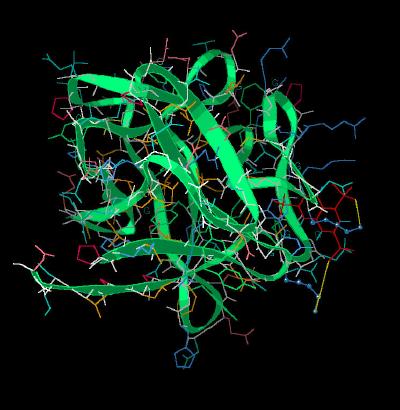
Kinemage 3: Lys Residues Binding To FGF 1
The nmr indicates that the sulfate groups of NTS interact with two Lysine residues (127 and 142)
View 1
the complex
View 2 the slot occupied by the inhibitor NTS.
View 3 offset view of NTS in the binding cavity.
|
173 K |
 |
| Click on KiNG to see | Lys Residues Interacting With NTS |
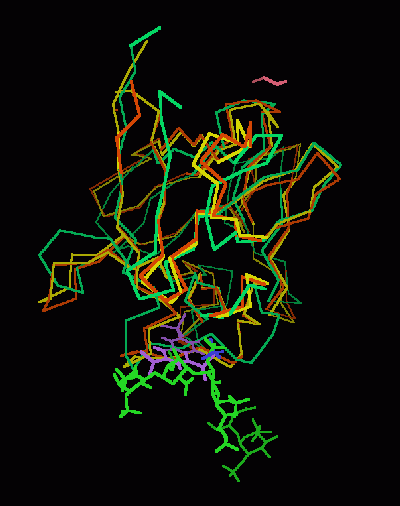
Kinemage 4: Comparison of FGF 1 Bound To NTS or Heparin
View 1 FGF 1 Bound To Heparin and FGF 1 Bound To NTS superimposed on FGF
2
View 2 the binding region
View 3 another angle of binding cavity.
Note that the NTS and heparin approach FGF in the same region of FGF. This is consistent with the observed competitive inhibition.
Also note the distortion of the backbone chain of FGF 1 that occurs when FGF 1 is bound to
NTS.
|
453 K |
 |
| Click on KiNG to see | FGF 1 Bound to NTS or Heparin |
Sequence: (Residues 24-154 of human FGF 1)
N-Terminal Not Present: AEGEITTFTALTEKFNLPPGNYK
Residue Core: KPKLLYCSNGGHFLRILPDGTVDGTRDRSDQHIQLQ
LSAESVGEVYIKSTETGQYLAMDTDGLLYGSQTPNEECLFLERLEENHYNTYISKKHAEK
NWFVGLKKNGSCKRGPRTHYGQKAILFLPLPVSSD
Source:
The human sequence was sub-cloned in plasmid pmg47 and expressed in escherichia coli; Structural Coordinates were determined by nmr and deposited in the Brookhaven Database File1RML. (The Brookhaven file contained 26 structures; only one was used in this kinemage). The heparin shown in kinemage 4 was taken from Brookhaven file 1AXM.
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences FGFR Sequences
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
Copyright 2005-2020 by Larry P. Taylor
Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute
University of Michigan
All Rights Reserved
Supported by the Pritzker Neuropsychiatric Disorders Research Consortium, and by NIH Grant 5 P01 MH42251, Conte Center Grant #L99MH60398, RO1 DA13386 and the Office of Naval Research (ONR) N00014-02-1-0879 to Huda Akil & Stanley J. Watson. at the Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute.