
|
The Rat Fibroblast Growth Factor 7 by Larry P. Taylor, Ph. D.
Feedback appreciated; please send comments to: Email: lpt Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute The University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI |
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences FGFR Sequences
The Rat Fibroblast Growth Factor 7
FGF 7 (also known as KFG for keratinocycte growth factor) is found in mesenchymal cells of parenchymal organs. It binds exclusively to a slice variant (IIIb) of the FGF Receptor 2 found in epithial cells. FGF 7 is more selective than FGF 1 and FGF 2 in binding to FGF receptors. Differences in sequence and geometry can rationalize this selectivity. A backbone comparison of FGF 7 overlaid upon FGF 2 is shown in Kinemage 6 .
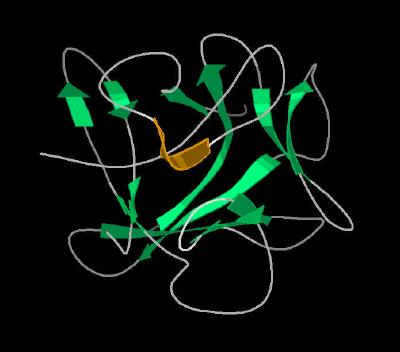
The crystal structure for FGF 7 ( Kinemage 1 ) was determined on a protein engineered from the rat sequence. The Clustal X alignment of human and rat FGF 7 sequences is shown below: A single molecule of FGF 7 is shown in Kinemage 2. The secondary structure cartoon of FGF 7 is shown in Kinemage 3.

The residues, except Ser-105 (which is X-ray unresolved), that are different between human and rat are Arg-38 (to Lys), Ser-40 (to Asn), Tyr-63 (to Phe), Ser-105 (to Asn), Leu-118 (to Ile), and Lys-121 (to Arg). These residues are highlighted in Kinemage 4. The Arg-35 implicated in high affinity binding of FGF 1 and FGF 2 is a glutamine in FGF 7. The characteristics of the unit cell for this structure are summarized at pdbsum.
Of particular interest is the portion of the molecule that is associated with low affinity binding (receptor discrimination loop) in the vicinity of the residues 102-107. In the receptor unbound FGF 7 molecule, this region is unresolved. This suggests a conformational mobility (especially compared to FGF 1 and FGF 2) that may be important in FGF receptor discrimination. This low affinity loop region is also a few residues longer which would present an altered (compared to FGF 1 and FGF 2) binding geometry to a FGF receptor.
Although FGF 7 shows the FGF conserved "hydrophobic patch" (Phe-16, Tyr-22, Tyr-94, Leu-135, Met-137), there is an additional "hydrophobic ridge" (Val-120, Thr-125, and Thr-131) which separates the overall surface charge of the "basic canyon" (Kinemage 7) into two distinct regions. In FGF 7, the primary heparin binding residues (Arg-18, Asn-92, Asn-114, Gln-115, Lys-124, Gln-129, and Lys-130) are separated by this "hydrophobic ridge" .In addition, FGF residue Glu-128 places a negative charge in the heparin binding region (as defined by FGF 1 and FGF 2) which would impair approach of strongly anionic species. This suggests that heparins (a wide variety of negatively charged sulfated sugars) would bind FGF 7 with a different geometry than binding to FGF 1 or FGF 2. The altered pattern of the heparin binding domain is most likely a strong factor in its specificity since the growth factor-heparin complex is a component of growth factor binding to its receptors. The hydrophobic patch is highlighted in Kinemage 5 .
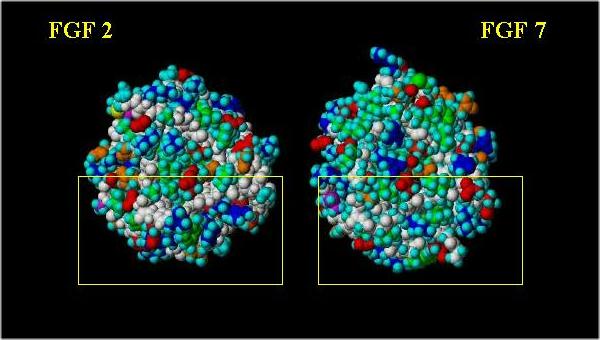
Space filling images (with the "basic canyon" surrounded by a yellow box) showing a front and side view comparison are shown below. Basic residues are blue; acidic residues are red; hydrophobics are green; neutral polar residues are orange; hydrogen atoms are cyan and the peptide backbone is white.
Note the difference in the pattern of the positively charged (blue) and hydrophobic (green) residues.
Side view of FGF 2 and FGF 7: "Basic Canyon"
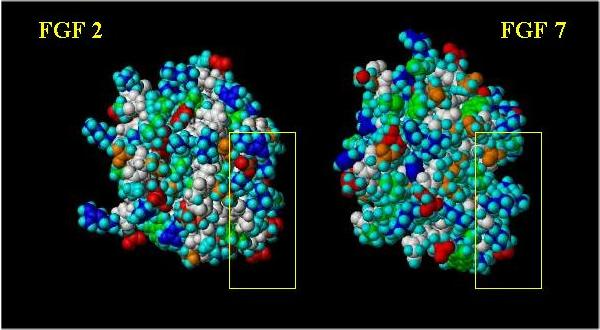
Front view of FGF 2 and FGF 7: "Basic Canyon"
The Kinemages
The real-time visualization using KiNG of the structures on this site requires a java-enabled (JRE from Java) browser.
Possible Icons to the left of molecular model image on the download page
| Java Not Activated | Java Not Activated | Java Functional |
 |
Blank Area
or message: Image requires a Java enabled browser
|
 |
| KiNG Inactive | KiNG Inactive | KiNG Full Functional |
A single click on the KiNG logo will launch the appropriate kinemage.
|
21 K |
 |
| Click On KiNG to see | Calpha Trace of FGF 7 Unit Cell |
Kinemage 2: The FGF 7 Molecule
|
204 K |
 |
| Click On KiNG to see | Ribbon Rendering of FGF 7 |
Kinemage 3: The Secondary Structure Cartoon Rendering
|
151 K |
 |
| Click On KiNG to see | Cartoon Rendering of FGF 7 |
Kinemage 4: Human and Rat Differences
The residues, except Ser-105 (which is X-ray unresolved), that are different between human and rat are Arg-38 (to Lys), Ser-40 (to Asn), Tyr-63 (to Phe), Ser-105 (to Asn), Leu-118 (to Ile), and Lys-121 (to Arg). The Arg-35 implicated in high affinity binding of FGF 1 and FGF 2 is a glutamine in FGF 7.
|
180 K |
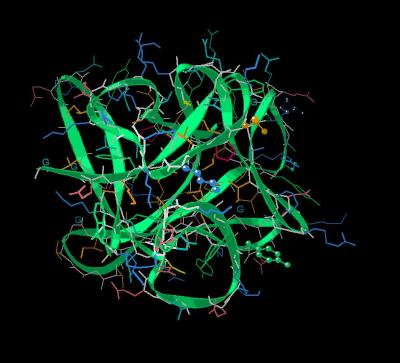 |
| Click On KiNG to see | Residues Different In Human Sequence |
Kinemage 5: The "Hydrophobic Patch"
The "hydrophobic patch" consists of residues Phe-16, Tyr-22, Tyr-94, Leu-135, and Met-137. Additional residues associated with binding (Gln-35 and Asn-92) are also shown.
View 1 FGF 7 monomer with binding residues highlighted
View 2 the "hydrophobic" patch of the high affinity binding region
View 3 the conserved Asn residue of the low affinity loop
|
181 K |
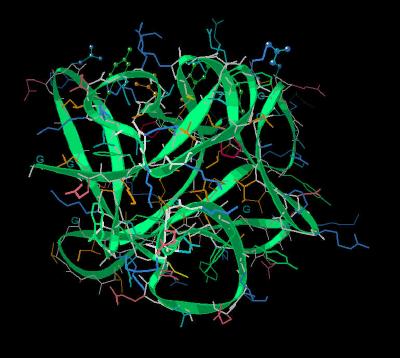 |
| Click On KiNG to see | The "Hydrophobic Patch" |
Kinemage 6: FGF 7 Superimposed Upon FGF 2
|
301 K |
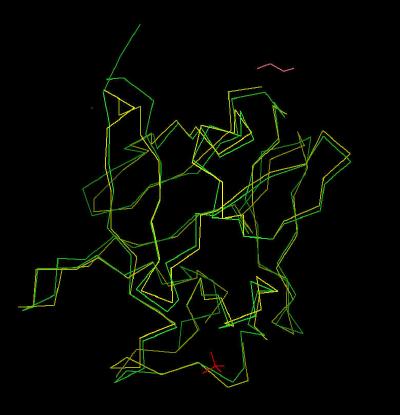 |
| Click On KiNG to see | Calpha Trace of FGF 7 Superimposed on FGF 2 |
Kinemage 7: The "Basic Canyon" of FGF 2 and FGF 7
The overlay of FGF 7 upon FGF 2 with "basic canyon" residues (Arg-18, Asn-92, Asn-114, Gln-115, Lys-124, Gln-129, and Lys-130) highlighted Also shown are those FGF 7 residues which would diminish or alter heparin binding (Hydrophobics: Val-120, Thr-125, and Thr-131 and negatively charged: Glu-128).
View 1
the complex
View 2 closer view of this canyon
|
358 K |
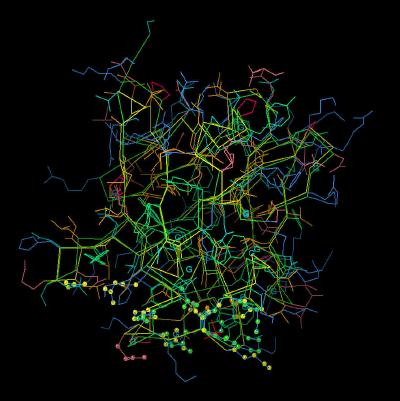 |
| Click On KiNG to see | Comparison of "Basic Canyon" of FGF 2 and FGF 7 |
Sequences: (X-ray Resolved residues span 9-140 of the rat FGF 19 sequence)
Unresolved N-Terminal: SYDYMEGG
X-Ray Resolved: DIRVRRLFCRTQWYLRIDKRGKVKGTQEMRNSYNIMEIRTVA
VGIVAIKGVESEYYLAMNKEGKLYAKKECNEDCNFKELILENHYNTYASAKW
Unesolved: THS
X-Ray Resolved: GGEMFVALNQKGLPVKGKKTKKEQKTAHFLPMAIT
The corresponding human sequence:
SYDYMEGGDIRVRRLFCRTQWYLRIDKRGKVKGTQEMKNNYNIMEIRTVAVGIVAIKG
VESEFYLAMNKEGKLYAKKECNEDCNFKELILENHYNTYASAKWTHNGGEMFVALNQK
GIPVRGKKTKKEQKTAHFLPMAIT
Source:
The rat FGF sequence was expressed in e.coli; The structural coordinates were taken from Brookhaven Database file 1QQK.
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences FGFR Sequences
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
Copyright 2005-2020 by Larry P. Taylor
Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute
University of Michigan
All Rights Reserved
Supported by the Pritzker Neuropsychiatric Disorders Research Consortium, and by NIH Grant 5 P01 MH42251, Conte Center Grant #L99MH60398, RO1 DA13386 and the Office of Naval Research (ONR) N00014-02-1-0879 to Huda Akil & Stanley J. Watson. at the Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute.