| Java Not Activated | Java Not Activated | Java Functional |
 |
Blank Area
or message: Image requires a Java enabled browser
|
 |
| KiNG Inactive | KiNG Inactive | KiNG Full Functional |
|
by Larry P. Taylor, Ph. D.
Feedback appreciated; please send comments to: Email: lpt Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute The University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI |
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences FGFR Sequences
Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 1 Bound To FGF Receptor 2c
This kinemage highlights the molecular architecture of acidic fibroblast growth factor
(FGF 1) interacting with the FGF 2 (splice variant IIIc) receptor.
The FGF 1 ligand to FGFR 2c interactions occur in three regions: the D2 and D3 domains as well as the short linker region between the two lobes of the total ligand binding domain. The general architecture of this interaction is shown in
the different rendering styles of Kinemage 1 (unit
cell Calphas) , Kinemage
2 (ribbons) , and Kinemage 3 (secondary structure
cartoon). The characteristics of the unit cell for this structure are summarized
at pdbsum.
A significant portion of the FGF ligand surface is buried in the ligand-receptor interface with approximately 39 of the 136 ligand residues (28.9 %) buried in the ligand binding volume defined by receptor domains D2 and D3. The heparin region
(Kinemage 7 ) is not hindered by this interaction and, as such, remains available to incoming heparin-like molecules.
The FGF 1 ligand to the FGFR 2c D2 domain interactions are primarily hydrophobic. They primarily involve high affinity ligand residues Tyr-15, Gly-20, Phe-22, Tyr-94. Leu-133 and Leu-135. Leu-133 and Leu-135 also form part of the hydrophobic pocket surrounding receptor linker region residue Arg-251. The D2 receptor residues involved in ligand binding are Lys-164, Leu-166, Ala-168, Val-169, and Pro-170. There are electrostatic interactions (enhanced by the surrounding hydrophobicity) between Arg-35 of the ligand to Glu-163 of the receptor. A similar salt bridge occurs between Arg-37 of the ligand and Asp-247 of the receptor. These are shown in
Kinemage 4.
The FGFR 2c linker region contains the critical residue, Arg-251. This receptor amino acid is surrounded by a hydrophobic pocket defined by ligand residues Leu-89, Leu-133 and Pro-134. This encircling volume of hydrophobicity enhances potential electrostatic and hydrogen bonding interactions. There is hydrogen bonding between the guanidinium group of receptor Arg-251 to the backbone carbonyl of ligand residue His-93. The combination of hydrophobic environment and the hydrogen bonding to His-93 places receptor Arg-251 in a position to form a strong hydrogen bond to ligand residue Asn-95. This is shown in
Kinemage 5. It has been shown that replacement of this FGF 1 residue Asn-95 with an alanine residue results in a 400 fold reduction in binding affinity.
The FGF ligand to FGF receptor domain D3 interactions are predominated by the ligand hairpin turn defined by beta sheets 4 and 5 sliding into a cleft of the FGF 2 receptor domain D3. (Kinemage 6 ).
A key feature of this interaction is the water-mediated hydrogen bond between FGF residue Tyr-8 and the backbone amide of receptor residue Val-280. This region has another hydrogen bond between FGF residue Asn-7 and the backbone carbonyl of receptor Val-280. The strength of this interaction is enhanced by surrounding receptor hydrophobics Val-280, Pro-286 and Ile-288.
A significant hydrophobic reaction occurs around receptor residue Val-317. The serves as a docking point for FGF ligand hydrophobic residues Tyr-55, Tyr-64, anhd Pro-79.
Another important residue is the invariant Glu-87. This residue is held in binding position by a hydrogen bond to ligand residue Tyr-97. Glu-87 then forms a an "anchoring" hydrogen bond to the backbone of the D3 domain at Gln-285 of the receptor.
The heparin binding region is dominated by a region of basic residues called the "basic canyon." The basic residues Lys-112, Lys-113, Lys-118, Arg-119, Arg-122, His-124, and Lys-128 are shown in
Kinemage 7.
The Kinemages
The real-time visualization using KiNG of the structures on this site requires a java-enabled (JRE from Java) browser.
Possible Icons to the left of molecular model image on the download page
| Java Not Activated | Java Not Activated | Java Functional |
 |
Blank Area
or message: Image requires a Java enabled browser
|
 |
| KiNG Inactive | KiNG Inactive | KiNG Full Functional |
A single click on the KiNG logo will launch the appropriate kinemage.
|
41 K |
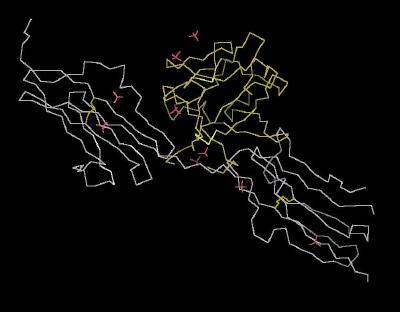 |
| Click On KiNG to see | Calpha Trace of the Unit Cell |
Kinemage 2: Ribbon Rendering of the FGF 1 Bound to FGFR 2c Complex
|
570 K |
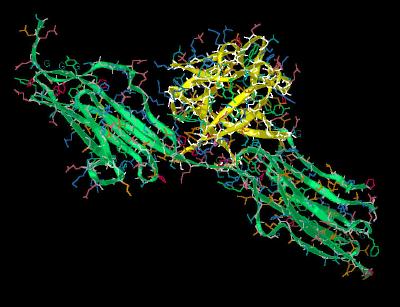 |
| Click On KiNG to see | Ribbon Rendering of FGF 1 Bound To FGFR 2c |
Kinemage 3: Cartoon Rendering of the FGF 1 Bound to FGFR 2c Complex
|
373 K |
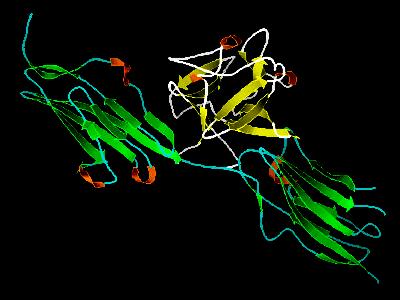 |
| Click On KiNG to see | Cartoon Rendering of FGF 1 Bound To FGFR 2c |
Kinemage 4: Interactions of FGF 1 at FGFR 2c Domain
D2
FGF 1 Interactions of FGF 1 at FGFR 2c Domain D2 include the high affinity residues Tyr-15, Arg-35, Asn-92, Tyr-94, Leu-133, & Leu-135.
View 1
the ligand-receptor complex.
View 2 closer view of the ligand-receptor interface
|
491 K |
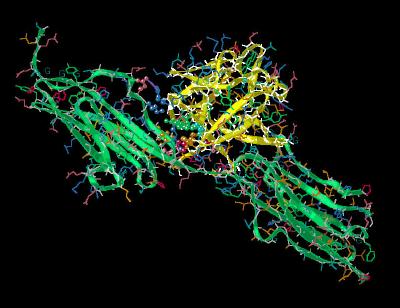 |
| Click On KiNG to see | FGF 1 Bound To FGFR 2c: Domain D2 Interactions |
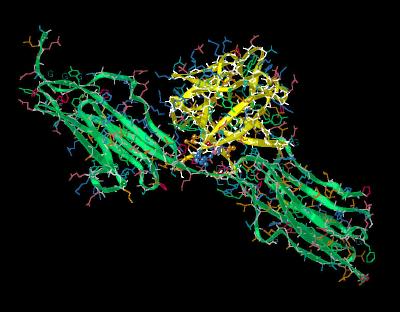
Kinemage 5: Interactions
between FGF 1 and the FGFR 2c Linker Between D2-D3
Interactions with FGF 1 at the FGFR 2c Linker between Domains D2 & D3 center around the invariant receptor residue Arg-251.
View 1 the ligand-receptor complex.
View 2 closer view
|
488 K |
 |
| Click On KiNG to see | FGF 1 Bound To FGFR 2c: Linker Interactions |
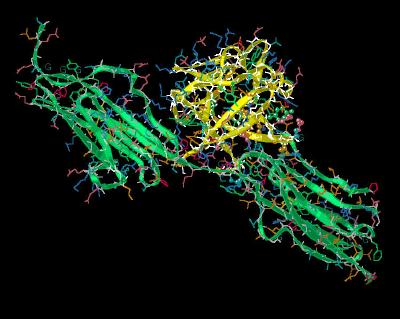
Kinemage 6: Interactions between FGF 1 and
the FGFR 2c D3 Domain
The FGF ligand to FGF receptor domain D3 interactions are predominated by the ligand hairpin turn defined by beta sheets 4 and 5 sliding into a cleft of the FGF 2 receptor domain
D3. FGF residue Tyr-8 hydrogen bonds to the backbone amide of receptor residue Val-280. This region has another hydrogen bond between FGF residue Asn-7 and the backbone carbonyl of receptor Val-280. The strength of this interaction is enhanced by surrounding receptor hydrophobics Val-280, Pro-286 and Ile-288.
Glu-87 is held in binding position by a hydrogen bond to ligand residue Tyr-97. Glu-87 then forms a an "anchoring" hydrogen bond to the backbone of the D3 domain at Gln-285 of the receptor.
A significant hydrophobic reaction occurs around receptor residue Val-317. The serves as a docking point for FGF ligand hydrophobic residues Tyr-55, Tyr-64,
and Pro-79.
View 1 the ligand-receptor complex.
View 2 highlights the binding cleft of the receptor D3 domain.
View 3 shows the hydrogen bonding of invariant ligand residue Glu-87.
View 4 highlights the hydrophobic contacts centered at receptor Val-317.
|
489 K |
 |
| Click On KiNG to see | FGF 1 Bound To FGFR 2c: Domain D3 Interactions |
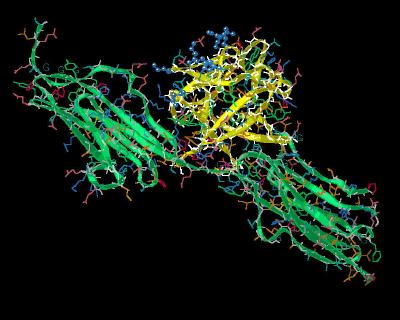
Kinemage 7: The "Basic Canyon" of FGF 1
The basic residues of the FGF 1 "Basic Canyon" are Lys-112, Lys-113, Lys-118, Arg-119, Arg-122, His-124, and Lys-128.
View 1 the ligand-receptor complex.
View 2 close up of the "basic canyon."
|
488 K |
 |
| Click On KiNG to see | The "Basic Canyon" of FGF 1 |
Sequences:
FGF 1 (Residues 6-140)
GNYKKPKLLYCSNGGHFLRILPDGTVDGTRDRSDQHIQLQLSAESVGEVYIKSTETGQYL
AXDTDGLLYGSQTPNEECLFLERLEENHYNTYISKKHAEKNWFVGLKKNGSCKRGPRTHY
GQKAILFLPLPVSSD
FGFR 2 (IIIc) Residues 147- 362:
TLEPEGAPYWTNTEKXEKRLHAVPAANTVKFRCPAGGNPXPTXRWLKNGKEFKQEHRIGG
YKVRNQHWSLIXESVVPSDKGNYTCVVENEYGSINHTYHLDVVERSPHRPILQAGLPANA
STVVGGDVEFVCKVYSDAQPHIQWIKHVEKNGSKYGPDGLPYLKVLKAAGVNTTDKEIEV
LYIRNVTFEDAGEYTCLAGNSIGISFHSAWLTVLPA
Source:
cDNA corresponding to the D2 and D3 domains (residues 153-377) of FGFR 2 (IIIc) were cloned into a pET22b vector and expressed in S. coli BL21. Structural coordinates for the protein were taken from Brookhaven Database File1DJS.
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences FGFR Sequences
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
Copyright 2005-2020 by Larry P. Taylor
Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute
University of Michigan
All Rights Reserved
Supported by the Pritzker Neuropsychiatric Disorders Research Consortium, and by NIH Grant 5 P01 MH42251, Conte Center Grant #L99MH60398, RO1 DA13386 and the Office of Naval Research (ONR) N00014-02-1-0879 to Huda Akil & Stanley J. Watson. at the Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute.