| Java Not Activated | Java Not Activated | Java Functional |
 |
Blank Area
or message: Image requires a Java enabled browser
|
 |
| KiNG Inactive | KiNG Inactive | KiNG Full Functional |
|
Human FGF 2 Bound To FGFR 1c Dimer by Larry P. Taylor, Ph. D.
Feedback appreciated; please send comments to: Email: lpt Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute The University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI |
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences FGFR Sequences
Human FGF 2 Bound To FGFR 1c Dimer
The unit cell of the FGF 2-FGFR 1c Dimer is displayed in different renderings in Kinemage
1 , Kinemage 2, and Kinemage 3 .The
characteristics of the unit cell for this structure are summarized at pdbsum.
Kinemage 4 highlights the FGF 2 to FGFR 1c Domain 2 interactions. Aside from a hydrogen bond from Tyr-24 of FGF 2 to the receptor backbone at Leu-165, the FGF to receptor interactions
that are in the D2 Domain region are primarily hydrophobic. The hydrophobic interactions involve the side chains of Tyr-24 and Met-142 contacting D2 residue Ala-167. Ligand residues Asn-102, Tyr-103, and Leu-140 form a hydrophobic contact with Pro-169 of the D2 Domain of the receptor. Leu-140 also contacts receptor linker region residue Val-248. Since Ala-167, Pro-169, and Val-248 of D2 are well conserved among the four mammalian FGF receptors, the hydrophobic surface of this volume of the receptor may represent a conserved interaction site.
The Ala-167 of FGFR 1c, which interacts with FGF 2 hydrophobic residues, is part of the HAV triad that is the hallmark of cell adhesion molecules.
While the Linker region between D2 and D3 is short, it is well conserved and thus, highly significant in ligand receptor binding. Arg-250 is invariant across the four FGF receptors. This Arg residue has its position maintained for ligand interaction by a network of hydrogen bonds that involves both D2 and D3 regions of the receptor. This network provides a fairly rigid and conserved ligand-receptor binding geometry. The guanidinium group of Arg-250 makes two hydrogen bonds with FGF2: one with the backbone carbonyl oxygen of Asn-102 and another with the side chain carbonyl oxygen of Asn-104. An Asn-104 side chain amide in FGF 2 is also engaged in an
intra-molecular hydrogen bond with Tyr-106, which in turn is hydrogen bonded to Glu-96, another invariant residue in the FGF ligand family. The side chain of Glu-96 is also hydrogen bonded to the backbone amide nitrogen of Gln-284 in the D3 domain of the receptor. The FGF 2 to
FGFR 1c linker binding interactions are shown in
Kinemage 5 .
In addition, the side chains of Val-248 in the D2-D3 linker and the Leu-98 of FGF 2 form a hydrophobic shelf for the aliphatic portion of the Arg-250 side chain. This, plus, the two
intra-molecular hydrogen bonds between the Arg-250 guanidinium group and the side chain carboxylate of Asp-282 in D3
(Kinemage 6 ) may provide a stabilized D2-Linker-D3 region to facilitate ligand binding.
The interactions between D3 and FGF2 ( Kinemage 6 ) occur near the linker region of the receptor. The side chain of Phe-17 in FGF 2 inserts into a shallow hydrophobic pocket
formed by Pro-285, Ile-287, and the aliphatic portions of the Glu-324 and
Asp-320 in the FGFR 1c D3 Domain . Also, the back-bone of Phe-17 hydrogen bonds to the Gln-284. The side chain of Lys-21 hydrogen bonds with the side chain of Gln-284 and the backbone of Asp-282.
Residues 56-60 of FGF 2 are in the vicinity of the FGFR 1c D3 Domain and also contribute to ligand binding. The side chain of Gln-56 makes two hydrogen bonds with Asp-320 of D3; one with its backbone amide nitrogen and another with the side
chain carboxylate group. In addition, the aliphatic portion of the Gln-56 side chain is in van der Waals contact with Gly-315. Ala-57 hydrophobically interacts with Pro-285 and Gly-315. Glu-58 hydrogen bonds to the carboxylate of the backbone amide of Val-316 and forms hydrophobic contacts with His-286 and Gly-315. The backbone of Glu-59 is in van der Waals contact with the side chain of His-286. The guanidinium group of Arg-60 hydrogen bonds to the backbone carbonyl oxygen of Asn-345. This region of FGF
2 (residues 56-60) is divergent among the 23 members of the FGF family
members, suggesting that these residues may confer a significant component of specificity to FGF binding to its receptors.
Without the ligand, Val-316 of the FGFR 1c D3 Domain would be exposed to solvent. However, when ligand-bound, Val-316 hydrophobically interacts with Val-88 of FGF 2. Mutagenesis studies suggest this is an important contact point.
Kinemage 7 highlights the region (with trapped sulfate ions in the crystal) that would bind heparin. The negative charges of the polyanionic heparin would be complemented by the positive charges of the "basic canyon" (a channel of primarily positively charged residues that form a depression on the surface of both receptor and ligand that would facilitate heparin binding). The highlighted receptor residues include Lys-160, Lys-163, Lys-172, Lys-175, and Lys-177. Unfortunately, in the absence of heparin the side chains of Lys-160, Lys-175, and Lys-177 are
disordered (only the side chains of Lys-163 and Lys-172 are ordered and chelate a sulfate ion located in the "basic canyon." This is why only one atom of the side chains of Chain C are resolved and highlighted in this kinemage). These lysines are considered to be the "low-affinity" heparin sites.
The "high-affinity" heparin-binding site on FGF 2 contains residues Asn-27, Lys-125, Gln-134, and Arg-120. These residues
are on the surface of FGF2 adjacent to the end of the "Basic Canyon." An ordered sulfate ion is bound in the high-affinity heparin-binding site of each of the two FGF 2 molecules in the dimer.
Kinemage 8 highlights the receptor to receptor residues that are important in ligand-receptor complex dimerization. The primary region of receptor to receptor contact is the D2 Domain. Across a 2-fold axis of the dimer, the Ala-171 side chain forms a hydrophobic contact with the corresponding Ala-171 side chain from the other receptor. Ala-171 and Lys-172 atoms are in van der Waals contact with the corresponding atoms of the adjacent receptor. Hydrogen bonds between the side chain of Thr-173 and the backbone nitrogen of Thr-173 of the other receptor and
salt bridges between the side chains of Lys-172 and Asp-218 stabilize the interface.
Kinemage 9 highlights the ligand-receptor interactions important for dimerization. In general, these interactions are neither specific nor conserved. The one interaction worth noting is a backbone-to-backbone hydrogen bond between ligand Pro-132 and Gly-204 of the receptor. There are also hydrophobic contact points at the beta
8-9 loop residues Glu-99, Ser-100, Asn-101 and the beta 10-11 loop residues Pro-132, Gly-133, Leu-138 with receptor D2 Domain residues Pro-199, Asp-200, Ile-203, Gly-204, Gly-205, Ser-219, and Val-221.
The side chain of Lys-26 in FGF 2 forms a salt bridge with the side chain of Asp-218 of the D2 Domain of the receptor. Since Lys-26 may be a heparin-binding residue, the here-observed interaction with Asp-218 may or may not occur in the presence of heparin.
Kinemage 10 shows the backbone superimposition of bound and unbound (from Brookhaven 1BFF) FGF 2. The primary difference appears to be in the secondary binding site around the Ser-Asn-Asn sequence. The differences are best seen by toggling on the side chains. In addition, FGF Compares sequences and backbones for many FGF species.
The Kinemages
The real-time visualization using KiNG of the structures on this site requires a java-enabled (JRE from Java) browser.
Possible Icons to the left of molecular model image on the download page
| Java Not Activated | Java Not Activated | Java Functional |
 |
Blank Area
or message: Image requires a Java enabled browser
|
 |
| KiNG Inactive | KiNG Inactive | KiNG Full Functional |
A single click on the KiNG logo will launch the appropriate kinemage.
Kinemage 1: The Unit Cell for Human FGF 2 Bound To FGFR 1c Dimer
|
39 K |
|
|
Click on KiNG to see |
Unit Cell: FGF2 Bound to FGFR 1c |
Kinemage 2: Unit Cell With Ribbon Rendering
|
1,102 K |
|
|
Click on KiNG to see |
Unit Cell: Ribbon Rendering |
Kinemage 3: Unit Cell With Cartoon Rendering
|
894 K |
|
|
Click on KiNG to see |
Unit Cell: Cartoon Rendering |
Kinemage 4: FGF 2 Ligand-D2 Receptor Interactions
The FGF 2 to FGFR 1c D2 interactions include a hydrogen bond from FGF 2 Tyr-24 to the receptor backbone at Leu-165, hydrophobic interactions Tyr-24 and Met-142 contacting D2 residue Ala-167. Ligand residues Asn-102, Tyr-103, and Leu-140 form a hydrophobic contact with Pro-169 of the D2 Domain of the receptor. Leu-140 also contacts receptor linker region residue Val-248.
View 1 the Complex
View 2 shows the Tyr-24 H-bond
View 3 shows the hydrophobic contacts
View 4 shows another view of the hydrophobic contacts
View 5 shows a third view of the hydrophobic contacts
|
943 K |
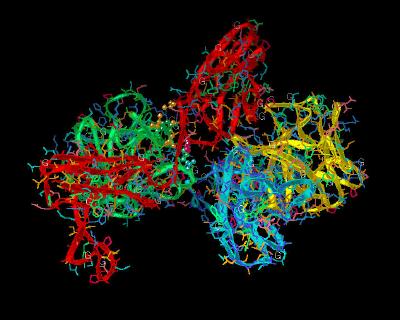 |
| Click on KiNG to see | FGF 2 Interactions With D2 Domain of FGFR 1c |
Kinemage 5: FGF 2 Ligand-Linker Receptor Interactions
The FGFR invariant Arg-250 hydrogen bonds with FGF 2: one with the backbone carbonyl oxygen of Asn-102 and another with the side chain carbonyl oxygen of Asn-104. An Asn-104 side chain amide in FGF 2 is also engaged in an intra-molecular hydrogen bond with Tyr-106, which in turn is hydrogen bonded to Glu-96, another invariant residue in the FGF ligand family. The side chain of Glu-96 is also hydrogen bonded to the backbone amide nitrogen of Gln-284 in the D3 domain of the receptor.
View 1 the Complex
View 2 shows the Hydrophobic contacts
View 3 shows the H Bonding scheme
View 4 is another view of the H Bonding
|
943 K |
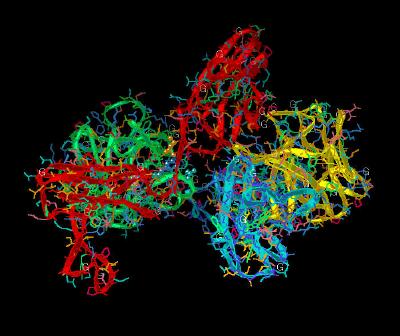 |
| Click on KiNG to see | FGF 2 Interactions With Linker Region of FGFR 1c |
Kinemage 6: FGF 2 Ligand-D3 Receptor Interactions
The Phe-17 in FGF 2 inserts into a shallow hydrophobic pocket formed by Pro-285, Ile-287, and the aliphatic portions of the Glu-324 and Asp-320 in the FGFR 1c D3 Domain . The back-bone of Phe-17 hydrogen bonds to the Gln-284. The side chain of Lys-21 hydrogen bonds with the side chain of Gln-284 and the backbone of Asp-282. Gln-56 makes two hydrogen bonds with Asp-320 of D3; one with its backbone amide nitrogen and another with the side chain carboxylate group. In addition, the aliphatic portion of the Gln-56 side chain is in van der Waals contact with Gly-315. Ala-57 hydrophobically interacts with Pro-285 and Gly-315. Glu-58 hydrogen bonds to the carboxylate of the backbone amide of Val-316 and forms hydrophobic contacts with His-286 and Gly-315. The backbone of Glu-59 is in van der Waals contact with the side chain of His-286. The guanidinium group of Arg-60 hydrogen bonds to the backbone carbonyl oxygen of Asn-345.
View 1 the Complex
View 2 shows the H Bonding network
View 3 shows another view of the H Bonding
View 4 highlights a third view of the H Bonding
View 5 shows the Val 316 (Receptor) - Val 88 (Ligand) contact
|
947 K |
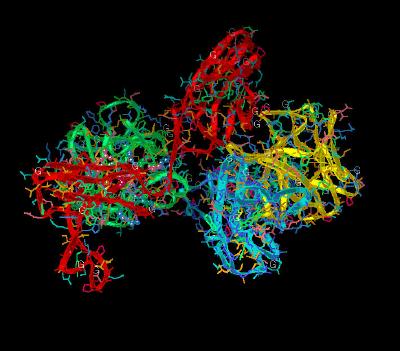 |
| Click on KiNG to see | FGF 2 Interactions With D3 Domain of FGFR 1c |
Kinemage 7: Heparin Binding Sites
Heparin binding sites are Lys-160, Lys-163, Lys-172, Lys-175, and Lys-177. Unfortunately, in the absence of heparin the side chains of Lys-160, Lys-175, and Lys-177 are disordered (only the side chains of Lys-163 and Lys-172 are ordered and chelate a sulfate ion located in the "basic canyon." The "high-affinity" heparin-binding site on FGF 2 contains residues Asn-27, Lys-125, Gln-134, and Arg-120.
View 1 the Complex
View 2 shows the "Basic Canyon"
View 3 another view of the "Basic Canyon"
|
942 K |
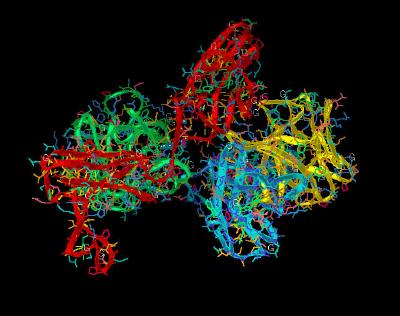 |
| Click on KiNG to see | Heparin Binding Sites |
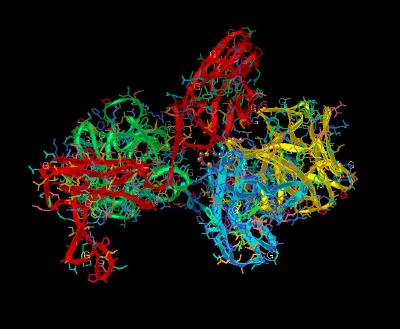
Kinemage 8: Receptor-Receptor Dimerization Sites
The Receptor-Receptor Dimerization Sites: Ala-171 and Lys-172 atoms are in van der Waals contact with the corresponding atoms of the adjacent receptor. Hydrogen bonds between the side chain of Thr-173 and the backbone nitrogen of Thr-173 of the other receptor and salt bridges between the side chains of Lys-172 and Asp-218 stabilize the interface.
View 1 the Complex
View 2 shows the dimerization interface
View 3 highlights the H Bonds and salt bridges
|
943 K |
 |
| Click on KiNG to see | Receptor-Receptor Dimerization Sites |
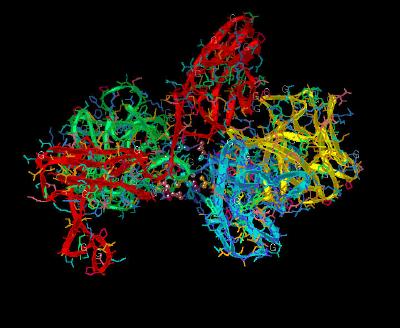
Kinemage 9: Ligand-Receptor Dimerization Sites
There is a hydrogen bond between ligand Pro-132 and Gly-204 of the receptor. There are also hydrophobic contact points at the beta
8-9 loop residues Glu-99, Ser-100, Asn-101 and the beta 10-11 loop residues Pro-132, Gly-133, Leu-138 with receptor D2 Domain residues Pro-199, Asp-200, Ile-203, Gly-204, Gly-205, Ser-219, and Val-221. The side chain of Lys-26 in FGF 2 forms a hydrogen bond with the side chain of Asp-218 of the D2 Domain of the receptor. Since Lys-26 may be a heparin-binding residue, the here-observed interaction with Asp-218 may or may not occur in the presence of heparin.
View 1 the Complex
View 2 highlights the Pro-Gly interaction
View 3 shows the hydrophobic interactions
View 4 shows the Lys-Asp salt bridge
|
944 K |
 |
| Click on KiNG to see | Ligand-Receptor Dimerization Sites |
Kinemage 10: Bound and Unbound FGF 2
The structure of FGF 2 bound (from structure 1CVS) superimposed upon unbound (from structure 1BFF) FGF 2.
View 1 the overlay
View 2 highlights the area of structural change upon binding (yellow backbone Ser-100, Asn-101, and Asn-102.)
|
393 K |
 |
| Click on KiNG to see | FGF 2 Bound & Unbound |
X-Ray Resolved Sequences:
Chains A & B: Residues 16-144 of Human FGF 2
Chains C & D: Residues 149-359 of Human FGFR 1c
Chain A FGF 2
GHFKDPKRLYCKNGGFFLRIHPDGRVDGVREKSDPHIKLQLQAEERGVVSIKGVSANRYL
AMKEDGRLLASKSVTDECFFFERLESNNYNTYRSRKYTSWYVALKRTGQYKLGSKTGPGQ
KAILFLPMSAKS
Chain B FGF 2
GHFKDPKRLYCKNGGFFLRIHPDGRVDGVREKSDPHIKLQLQAEERGVVSIKGVSANRYL
AMKEDGRLLASKSVTDECFFFERLESNNYNTYRSRKYTSWYVALKRTGQYKLGSKTGPGQ
KAILFLPMSAKS
Chain C FGFR 1c
TDNTKPNRMPVAPYWTSPEKMEKKLHAVPAAKTVKFKCPSSGTPQPTLRWLKNGKEFKPD
HRIGGYKVRYATWSIIMDSVVPSDKGNYTCIVENEYGSINHTYQLDVVERSPHRPILQAG
LPANKTVALGSNVEFMCKVYSDPQPHIQWLKHIEVNGSKIGPDNLPYVQILKTAGVNTTD
KEMEVLHLRNVSFEDAGEYTCLAGNSIGLSHHSAWLTVLEALEER
Chain D FGFR 1c
TDNTKPNRMPVAPYWTSPEKMEKKLHAVPAAKTVKFKCPSSGTPQPTLRWLKNGKEFKPD
HRIGGYKVRYATWSIIMDSVVPSDKGNYTCIVENEYGSINHTYQLDVVERSPHRPILQAG
LPANKTVALGSNVEFMCKVYSDPQPHIQWLKHIEVNGSKIGPDNLPYVQILKTAGVNTTD
KEMEVLHLRNVSFEDAGEYTCLAGNSIGLSHHSAWLTVLEALEER
Source:
The human sequence corresponding to residues 142-365 of the receptor was expressed in escherichia coli; Structural coordinates from Brookhaven Database
file1CVS..
FGF Site: FGF Intro
Nomenclature Notes
References FGF
Sequences FGFR Sequences
My
University Home Harris
Links Chemistry
/ Modeling Links
Copyright 2005-2020 by Larry P. Taylor
Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute
The University of Michigan
All Rights Reserved
Supported by the Pritzker Neuropsychiatric Disorders Research Consortium, and by NIH Grant 5 P01 MH42251, Conte Center Grant #L99MH60398, RO1 DA13386 and the Office of Naval Research (ONR) N00014-02-1-0879 to Huda Akil & Stanley J. Watson. at the Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute.