| Java Not Activated | Java Not Activated | Java Functional |
 |
Blank Area
or message: Image requires a Java enabled browser
|
 |
| KiNG Inactive | KiNG Inactive | KiNG Full Functional |
|
The Human Basic Fibroblast Growth factor (FGF 2) by Larry P. Taylor, Ph. D.
Feedback appreciated; please send comments to: Email: lpt Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute The University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI |
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences FGFR Sequences
The Human Basic Fibroblast Growth factor (FGF 2)
Basic FGF (FGF 2) is one of the best characterized FGF molecular structures. The Calpha trace of unit cell is shown in Kinemage 1. Addition of side chains and a ribbon cartoon of the structure is shown in Kinemage 2. The FGF ligand molecules all share a characteristic architecture: the beta trefoil (three-fold repeat of a four-stranded sheet assembly without extended alpha helix strands possessing a pseudo three-fold axis of symmetry) motif. This motif is highlighted in Kinemage 3. There is a disulphide bond between the peptide chain residue Cys-77 and a beta-mercaptoethanol (bme) molecule. The beta-mercaptoethanol was added to the crystallization buffer to prevent disulphide mediated polymerization during crystallization. The characteristics of the unit cell for this structure are summarized at pdbsum.
Many of the 67 ordered waters have locations conserved across similar FGF molecules. This suggests a relatively rigid protein structure with possible water-mediated hydrogen bonding within the FGF playing a role in either structure of the protein itself or in the protein's interaction with its receptor or other molecules.
The crystal shows an ordered phosphate ion held by residues Asn-35, Arg-28, and Lys-133 ( Kinemage 4) that resides in the vicinity of the "basic canyon" (Kinemage 6) that is associated with heparin binding to the FGF molecule.
There are two distinctly different binding regions ( Kinemage
5 ) on the surface of the FGF molecule that are involved in FGF receptor binding. The primary high affinity binding site is a non-contiguous surface arrangement of FGF 2 residues Tyr-32, Asn-35, Arg-52, Tyr-111, Leu-148,
Pro-149, and Met-158. The lower affinity region is a contiguous loop of residues with residues Arg-117, Lys-118, Tyr-119, Thr-120, Ser-121 and Trp-122. The low affinity loop varies in size and sequence across the various FGF molecules. This suggests that this region of the molecule is involved in selectively or differentiation.
Basic FGF (FGF 2) shows a local surface concentration of predominately positively charged residues that has been called the "Basic Canyon."
These residues (Asn-35, Lys-127, Arg-128, Lys-133, Lys-137, Gln-142, and Lys-143) are complimentary to the poly-anion structure of
heparin and stabilize the formation of an FGF-heparin complex.
This canyon is shown in Kinemage 6.
The human gene for FGF 2 encodes a 155 residue protein. However, because of N-terminal enzymatic degradation, protein isolation schemes from biological sources typically shorten the full sequence to 140-146 residues. Thus, biological activity studies have been primarily carried out on a protein of 146 residues. This specific protein (1BFF) was isolated from cDNA encoding the full gene. This 154 residua protein shows no difference in biological activity compared to previously isolated shorter forms of
FGF 2. The X-ray diffraction experiment on the 154 residue basic FGF only resolves positions 26-154 because of N-terminal conformational mobility which does not provide an interpretable x-ray diffraction pattern.
The Kinemages
The real-time visualization using KiNG of the structures on this site requires a java-enabled (JRE from Java) browser.
Possible Icons to the left of molecular model image on the download page
| Java Not Activated | Java Not Activated | Java Functional |
 |
Blank Area
or message: Image requires a Java enabled browser
|
 |
| KiNG Inactive | KiNG Inactive | KiNG Full Functional |
A single click on the KiNG logo will launch the appropriate kinemage.
Kinemage 1: The "Classic" Kinemage
This is an alpha carbon trace of the peptide backbone for basic FGF
|
12 K |
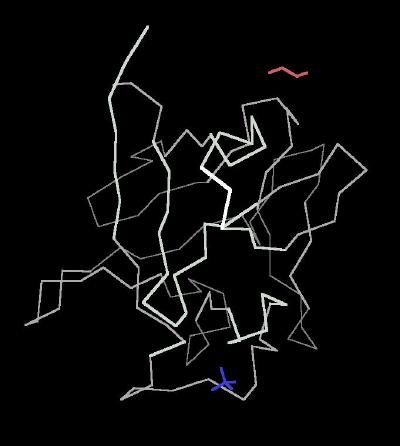 |
| Click On KiNG to see | Calpha Carbon Trace of Basic FGF |
Kinemage 2: Ribbon Rendering of the Basic FGF Molecule
|
260 K |
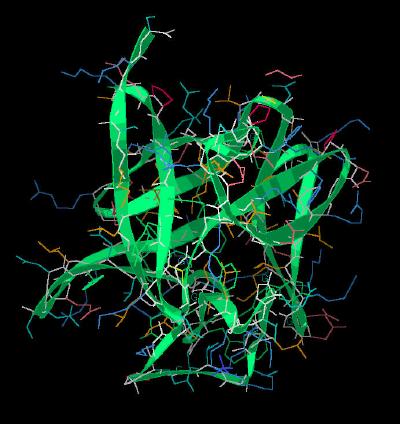 |
| Click On KiNG to see | Ribbon Rendering of Basic FGF |
Kinemage 3: The Trefoil Architecture
The ribbon rendering highlights the three distinct groups of four beta sheets
each that comprise the trefoil motif. The three folds are depicted
as Fold 1 (Red), Fold 2 (Yellow) and Fold 3 (Blue) with each
separate beta sheet individually visible via toggle buttons. The base of the trefoil (sheets
1, 4, 5, 8, 9, & 12) form a beta barrel motif.
The Beta Sheets Of the Trefoil Motif
|
Fold 1 |
Fold 2 |
Fold 3 |
| Sheet | Residues | Sheet | Residues | Sheet | Residues |
| 1 | 28-34 | 4 | 60-67 | 8 | 101-107 |
| 2 | 37-4 | 5 | 59-76 | 9 | 110-117 |
| 3 | 46-51 | 6 | 79-85 | 10 | 122-127 |
| 12 | 146-152 | 7 | 89-93 | 11 | 130-133 |
View 1 ribbon only rendering of FGF 2 highlighting the trefoil architecture.
View 2 shows the molecule rotated to emphasize the three distinctive folds of the trefoil architecture. This arrangement is maintained by the fold (in red) in which the two beta sheets 1 and 12 bring together the C and N-terminal ends of the protein. The stability of the this junction may play a key role in regulation of this
molecule.
|
310 K |
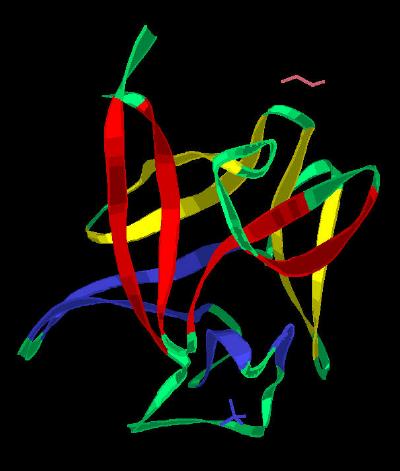 |
| Click On KiNG to see | The beta Sheets of Basic FGF |
Kinemage 4: The Apparent Phosphate Ion Binding
Site
View 1 highlights phosphate binding residues Asn-35, Arg-28,
and Lys-133,
View 2 a closer view
|
254 K |
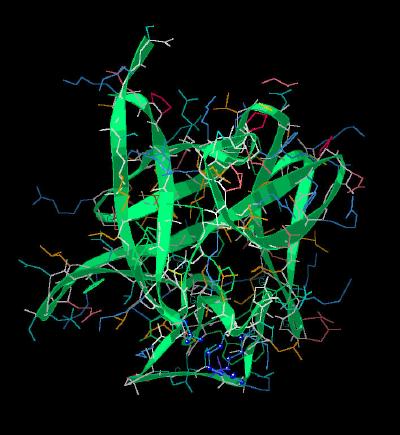 |
| Click On KiNG to see | Phosphate Binding Site |
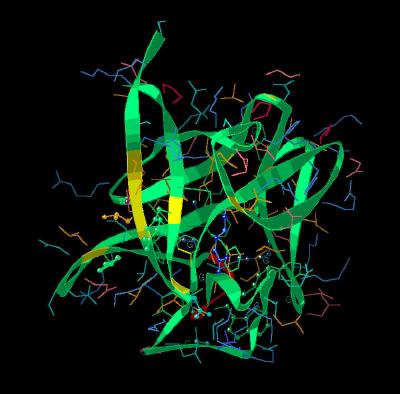
Kinemage 5: The Receptor Binding Regions
There are two distinctly different binding regions on the surface of the FGF molecule that are involved in FGF receptor binding. The primary high affinity binding site is a non-contiguous surface arrangement of residues comprised of Tyr-32, Asn-35, Arg-52, Tyr-111, Leu-148, Pro-149, and Met-158. The lower affinity region is a contiguous loop of residues with residues Arg-117, Lys-118, Tyr-119, Thr-120, Ser-121 and Trp-122.. The low affinity loop varies in size and sequence across the various FGF molecules. This suggests that this region of the molecule is involved in selectively or differentiation.
View 1 FGF 2 molecule showing high (Yellow Ribbon Strips ) and low (Red
Ribbon Strip) affinity binding regions.
View 2 demonstrates that the high and low affinity binding regions are on opposite surfaces of the molecule
View 3 highlights the non-contiguous region of the high affinity site.
View 4 highlights the low affinity loop region.
|
232 K |
 |
| Click On KiNG to see | Receptors Binding Sites of Basic FGF |
Kinemage 6: The "Basic Canyon" of Basic FGF (FGF 2)
Basic FGF with the residues implicated in heparin binding are Asn-35, Lys-127, Arg-128, Lys-133, Lys-137, Gln-142, and Lys-143.
View 1 highlights the "Basic Canyon"
View 2 close-up of the "Basic Canyon."
|
229 K |
|
| Click On KiNG to see | Heparin Binding Sites of Basic FGF |
Sequence: (The X-Ray resolved residues are 26-154 of the human FGF 2 sequence.)
Unresolved N-Terminal: AAGSITTLPALPEDGGSGAFPPGHF
X-Ray Resolved: KDPKRLYCKNGGFFLRIHPDGRVDGVREKSDPH
IKLQLQAEERGVVSIKGVCANRYLAMKEDGRLLASKCVTDECFFFERLE
SNNYNTYRSRKYTSWYVALKRTGQYKLGSKTGPGQKAILFLPMSAKS
Source:
The human sequence was expressed in escherichia coli; Structural Coordinates were taken from the Brookhaven Data Base File1BFF.
FGF Site: FGF Intro Nomenclature Notes References FGF Sequences FGFR Sequences
My University Home Harris Links Chemistry / Modeling Links
Copyright 2005-20020 by Larry P. Taylor
Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute
University of Michigan
All Rights Reserved
Supported by the Pritzker Neuropsychiatric Disorders Research Consortium, and by NIH Grant 5 P01 MH42251, Conte Center Grant #L99MH60398, RO1 DA13386 and the Office of Naval Research (ONR) N00014-02-1-0879 to Huda Akil & Stanley J. Watson. at the Molecular & Behavioral Neuroscience Institute.