Bi-linear
reduced-order modeling (BLM) is an effective method for vibration
problem of elastic structures with intermittent contact nonlinearity
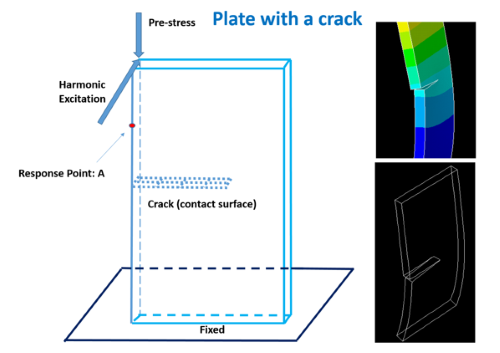
(e.g. the simplest case is a plate with a crack). The rationale at the
basis of this technique is that, in a given frequency range of
interest, displacement of structure can be approximated by linear
superposition of two sets of linear constraint modes of specific
contact boundary conditions (BCs) (that is, a specific part of contact
surface is closed and the rest is open, and the opposite situation).
Contact BCs of the two sets of modes have essential effect on the
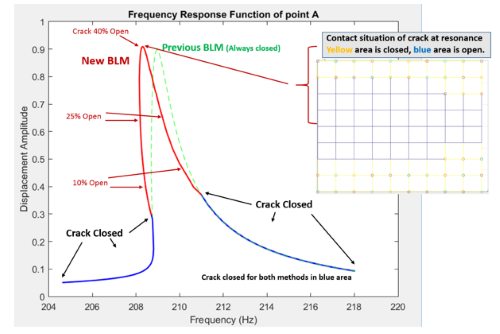
accuracy of this method. Previous bi-linear reduced-order method
assumes that BCs of contact surfaces are always the same, but in fact
they would changes with frequency of excitation. The goal of this
research is to set up a new adaptive contact surface calculating method
for bi-linear reduced-order modeling which can calculate and update
contact BCs of structure at any specific frequency. Our research may
improve the accuracy of bi-linear reduced-order modeling method to a
considerable extent.
|


