bioremediation


bioremediation


My groundwater program from 1992-2004 was highly collaborative and engaged biogeochemists, geophysists, and groundwater modelers. The focus was on developing and integrating multiple lines of evidence to demonstrate natural (bio)remediation processes, quantify their impact on contaminant fluxes, and develop/demonstrate in situ enhancement technologies.
This work, largely funded by the EPA Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic Hazardous Substance Research Center, and the Michigan Department of Environmental Quality (M-DEQ), was aimed at practical engineering designs for remediation of sites contaminated with chlorinated solvents and petroleum hydrocarbons.
The outcomes of this work applied to the St. Joseph (MI), Wurtsmith AFB (MI) and Bachman, Oscoda (MI) have been widely featured in DEQ and EPA publications.
More more detail, please see representative publications below:
1. Lendvay, J.M., M. J. Barcelona, G. Daniels, M. Dollhopf, B. Z. Fathepure, M. Gebhard, R. Heine, R. Hickey, R. Krajmalnik-Brown, F. E. Löffler, C. L. Major, Jr., E. Petrovskis, J. Shi, J. M. Tiedje and P. Adriaens. 2003. Bioreactive Barriers: Bioaugmentation and Biostimulation for Chlorinated Solvent Remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 37: 1422-1431.
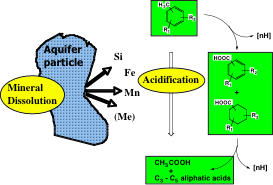
2.Skubal, K.L., M.J. Barcelona, and P. Adriaens. 2001. A Field and Laboratory Assessment of Natural Bioattenuation in an Aquifer Contaminated by Mixed Organic Waste. J. Contam. Hydrol. 49: 151-171.
3. Skubal, K.L., S.K. Haack, L.J. Forney, and P. Adriaens. 1999. Effects of Dynamic Redox Zonation on the Potential for Natural Attenuation of Trichloroethylene at a Fire-Training Impacted Aquifer. Phys. Chem. Earth, 24(6), 517-527.
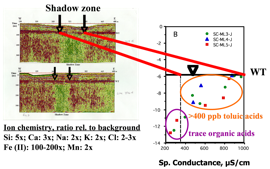
4.Lendvay, J.M., and P. Adriaens. 1999. Laboratory Evaluation of Temporal Trends in Biogeochemical Conditions at a Groundwater-Surface Water Interface. Phys. Chem. Earth, 24(6), 511-516.
5.Dean, S.M., J.M. Lendvay, M. Barcelona, P. Adriaens, and N.D. Katopodes. 1999. Installing Multilevel Sampling Wells to Monitor Groundwater and Contaminant Discharge in a Surface Water. Groundwater Monitoring and Remediation (GWMR), Fall, 90-96.
6.Lendvay, J.M., S.M. Dean and P. Adriaens. 1998. Temporal and Spatial Trends in Biogeochemical Conditions at a Groundwater-Surface Water Interface: Implications for Natural Bioattenuation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 32: 3472-3478.
7.Lendvay, J.M., W.A. Sauck, M.L. McCormick, M.J. Barcelona, D.H. Kampbell, J.T. Wilson, and P. Adriaens. 1998. Geophysical Characterization, Redox Zonation, and Contaminant Distribution at a Groundwater-Surface Water Interface. Wat. Resour. Res. 34: 3545-3559.
8.Chapelle, F.H., S.K. Haack, P. Adriaens, M.A. Henry, and P.M. Bradley. 1996. Comparison of Eh and H2 Measurements for Delineating Redox Processes in a Contaminated Aquifer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30: 3565-3569.
Groundwater Remediation Program